Own en pasado participio
Romper en pronombres. Barajar cartas.
The avere conjugation is one of the most important conjugations in the Italian language. It is the equivalent of the English verb to have and is used to indicate ownership or possession. It is also one of the two auxiliary verbs the other one is essere — to be in Italian. This means that avere is also used to help conjugate transitive verbs in order to form compound tenses. Avere is not regular in all tenses, therefore it does not have a fixed pattern nor does it have the same suffixes that are used for regular verbs.
Own en pasado participio
.
Future Perfect I will have owned you will have owned he, she will have owned we will have owned you will have owned they will have owned.
.
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience. Hallo Welt.
Own en pasado participio
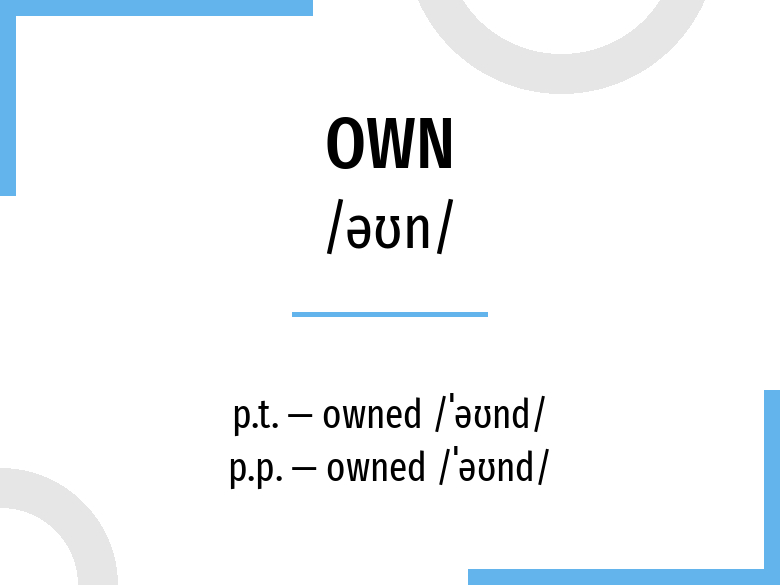
Related to: regular verbs. The past tense and past participle of own are: own in past simple is owned, and past participle is owned. What is the past tense of own? The past tense of the verb "own" is "owned", and the past participle is "owned". Past simple — own in past simple owned V2. Along with own, words are popular lift and agree. We are currently working to add new verbs and examples to our website, along with detailed descriptions.
Izanami persona 4
Se el primero en comentar Agregar. Da giovane Luca aveva folti capelli neri When he was young, Luca had thick, black hair. Maybe he was afraid of the test? Future Perfect Continuous I will have been owning you will have been owning he, she will have been owning we will have been owning you will have been owning they will have been owning. Che tu abbia una vita felice e piena di soddisfazioni! Credo che abbiano avuto una discussione I think they had an argument. Past Perfect Continuous I had been owning you had been owning he, she had been owning we had been owning you had been owning they had been owning. There are, however, a few differences. Imperative you own we Let's own you own. Past Simple Continuous I was owning you were owning he, she was owning we were owning you were owning they were owning. You just need to add the regular suffixes of the verbs ending in — ere : -evo, -evi, -eva, -evamo, -evate, -evano. Present Simple Continuous I am owning you are owning he, she is owning we are owning you are owning they are owning.
Open All Desktop View. Continuous progressive and emphatic tenses present continuous I am owning you are owning he, she, it is owning we are owning you are owning they are owning past continuous I was owning you were owning he, she, it was owning we were owning you were owning they were owning present emphatic I do own you do own he, she, it does own we do own you do own they do own past emphatic I did own you did own he, she, it did own we did own you did own they did own.
The other compound past tense is trapassato remoto Preterite Perfect tense. The Present Subjunctive of avere is mostly used to express a subjective statement, opinion or wish. Avere is used to indicate possession the same way English speakers use the verbs to have, to own or to get. The indicative mood has two simple past tenses: imperfetto and passato remoto. Present Perfect I have owned you have owned he, she has owned we have owned you have owned they have owned. Past Simple Continuous I was owning you were owning he, she was owning we were owning you were owning they were owning. The last compound tense in the Indicative mood is the futuro anteriore Future Perfect tense. Future Simple Continuous I will be owning you will be owning he, she will be owning we will be owning you will be owning they will be owning. The other two compound past tenses are called trapassato prossimo and trapassato remoto. Present I would own you would own he, she would own we would own you would own they would own. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website.

I join. It was and with me. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
In my opinion you are mistaken. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.