Ph responsive polymers
KocakC. Tuncer and V. E-mail: gkocak ogu.
In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, etc. In the last two decades, there have been great developments in synthetic methods and strategies for the preparation of novel pH-responsive polymers or polymeric materials providing possible materials for various applications including biotechnology, nanotechnology, colloid and surface science, materials science, etc. Kocak, C. Tuncer and V. To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page. If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
Ph responsive polymers
Materials may swell, collapse, or change depending on the pH of their environment. This behavior is exhibited due to the presence of certain functional groups in the polymer chain. These polymers can be designed with many different architectures for different applications. Key uses of pH sensitive polymers are controlled drug delivery systems, biomimetics , micromechanical systems, separation processes, and surface functionalization. The mechanism of response is the same for both, only the stimulus varies. The general form of the polymer is a backbone with functional "pendant groups" that hang off of it. Repulsions between like charges cause the polymers to change shape. Polyacids, also known as anionic polymers, are polymers that have acidic groups. Polyacids accept protons at low pH values. At higher pH values, they deprotonate and become negatively charged. This swelling behavior is observed when the pH is greater than the pKa of the polymer. Polybases are the basic equivalent of polyacids and are also known as cationic polymers. They accept protons at low pH like polyacids do, but they then become positively charged.
Such ionizations cause their swelling due to an increase in hydrophilicity of related groups, ph responsive polymers, changes in osmolarity and ionic interactions within the gel. In the second strategy, polymeric materials release drugs with cleavage of covalent bonds between the drug and polymer by pH changes.
.
Kocak , C. Tuncer and V. E-mail: gkocak ogu. In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, etc. In the last two decades, there have been great developments in synthetic methods and strategies for the preparation of novel pH-responsive polymers or polymeric materials providing possible materials for various applications including biotechnology, nanotechnology, colloid and surface science, materials science, etc. He is currently a PhD student in Prof. Butun's research group at Eskisehir Osmangazi University. His current research interests include block copolymers, post-polymerization modifications, cross-linked micelles, water-soluble polymers, hydrogels, stimulus-responsive polymers and their applications.
Ph responsive polymers
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. This review summarizes the development of pH-responsive polymers and their main applications. Random pH-responsive copolymers have been prepared via conventional free radical polymerization from a pH-responsive pendant fatty acid-containing monomer AaU and a permanent water-soluble pendant sulfonate-containing monomer AMPS. The surfaces of the unimer micelles are covered with hydrophilic AMPS units, which provide colloidal stabilization. Through the use of a pH-responsive AaU homopolymer, pH-responsive sunscreen was developed.
Leo valdez
The micelles had a high amount of drug encapsulation capability within the small size. These cross-linked micelles like nanogels can swell or deswell by pH changes and might be useful in drug release studies as releasing systems. The glucose oxidase-catalyzed hydrolyzation of glucose produces gluconic acid, resulting in shrinking and a corresponding mass decrease in the pH-responsive polymer. Kocak , a C. Biodegradable microgel systems based on glycerol-1,3-diglycidyl ether cross-linked TEMPO-oxidized potato starch polymers are capable of absorbing a large amount of lysozyme. This repulsion leads to a swelling of the polymer. The copolymer has shown proton dissociation and dual ionic character. The rapidly increasing interest in functional materials with reversibly switchable physicochemical properties has led to significant work on the development of stimuli-responsive membranes, for which mass transfer and interfacial properties can be adjusted using external stimuli: temperature, pH, etc. Cited by. Jump to main content. As an example, the pH sensitivity of PEGMP brushes bearing orthophosphoric acid with two ionization states for switching surface wettability p K a1 in the range of pH 1—2 and p K a2 in the range of pH 6—7 has been well documented Fig. This study is a good report on the reversible transition from worm-like micelles to spherical micelles depending on pH change Fig.
In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, etc. In the last two decades, there have been great developments in synthetic methods and strategies for the preparation of novel pH-responsive polymers or polymeric materials providing possible materials for various applications including biotechnology, nanotechnology, colloid and surface science, materials science, etc.
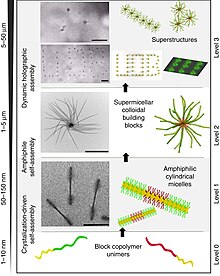
Therefore, more protein molecules are required to neutralize for the charge on the gel and the binding capacity increases. Vinyl, meth acrylamide, and meth acrylate polymers containing tertiary amine groups have also received great attention. These groups on polymers can also be modified to obtain different polymeric materials. This study is a good report on the reversible transition from worm-like micelles to spherical micelles depending on pH change Fig. The drug is delivered to the colonic region with a copolymer at pH 7. To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page. It shrinks or swells in response to decreasing or increasing pH values due to the dissociation of the branch carboxylic group at basic pH values. DOX has been chosen as a model hydrophobic drug. Boronic acids. This is due to the protein binding capacity which is mainly determined by charge compensation: with increasing pH, the positive charge on lysozyme decreases, while the negative charge on the microgel particle increases.

Curiously....