Ploidy
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The ability of an organism to replicate and segregate its genome with high fidelity is vital to its survival and for the production of future generations, ploidy. Errors in either ploidy these steps replication or segregation can lead to a change in ploidy or chromosome number, ploidy.
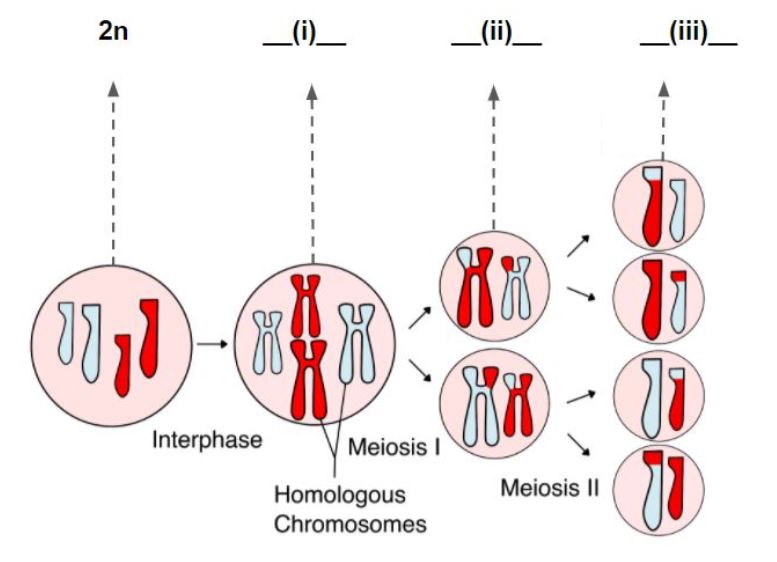
Definition noun, plural: ploidies The number of sets of homologous chromosomes that make up the genome of a cell or an organism Supplement Ploidy refers to the number of sets of homologous chromosomes in the genome of a cell or an organism. Each set is designated by n. Accordingly, one set of chromosome s, 1n , is described as monoploid. However, the term haploid is used to describe gametes that contain only half of the set of the usual sets of chromosomes of the somatic cells of an organism. The union of two haploid gametes, i. The two sets of chromosomes would be homologous chromosomes, i.
Ploidy
Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells , tissues , and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present the "ploidy level" : monoploid 1 set , diploid 2 sets , triploid 3 sets , tetraploid 4 sets , pentaploid 5 sets , hexaploid 6 sets , heptaploid [2] or septaploid [3] 7 sets , etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half of all known plant genera contain polyploid species, and about two-thirds of all grasses are polyploid. In some species, ploidy varies between individuals of the same species as in the social insects , and in others entire tissues and organ systems may be polyploid despite the rest of the body being diploid as in the mammalian liver. For many organisms, especially plants and fungi, changes in ploidy level between generations are major drivers of speciation. In mammals and birds, ploidy changes are typically fatal. Humans are diploid organisms, normally carrying two complete sets of chromosomes in their somatic cells: one copy of paternal and maternal chromosomes, respectively, in each of the 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes that humans normally have. This results in two homologous pairs within each of the 23 homologous pairs, providing a full complement of 46 chromosomes. This total number of individual chromosomes counting all complete sets is called the chromosome number or chromosome complement.
Zygoidy ploidy the state in which the chromosomes are paired and can undergo meiosis.
Not all plant species are diploids. Major crops, such as wheat, alfalfa, potato, cotton, and sugarcane, are polyploids. There are also plants that do not possess complete sets of chromosomes. Aneuploids have abnormal numbers of chromosomes and vary by the addition or deletion of specific individual chromosomes that otherwise would be present in the normal crop genome. Ploidy reduction produces haploids , which have only a single set of homologous chromosomes instead of the pair found in their diploid counterparts. Haploid plants are very valuable in certain breeding applications.
Cell division cycle, figure from Wikipedia. Cells that stop dividing exit the G1 phase of the cell cycle into a so-called G0 state. Cells reproduce genetically identical copies of themselves by cycles of cell growth and division. The cell cycle diagram on the left shows that a cell division cycle consists of 4 stages:. Chromosomes were first named by cytologists viewing dividing cells through a microscope. The modern definition of a chromosome now includes the function of heredity and the chemical composition. A chromosome is a DNA molecule that carries all or part of the hereditary information of an organism.
Ploidy
Aleeza C. Gerstein, Sarah P. Genomes vary dramatically in size and in content. This variation is driven in part by numerous polyploidization events that have happened over the course of eukaryotic evolution. Experimental evolution studies, primarily using the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae , provide insights into the immediate fitness effects of ploidy mutations, the ability of organisms of different ploidy levels to mask deleterious mutations, the impact of ploidy on rates of adaptation, and the relative roles of selection versus drift in shaping ploidy evolution.
Gas range cover
For example, tetraploid S. Analysis of the previously obtained transcriptome of HPT2 and RPT1 10 confirmed that these expression changes were not due to reduced transcription of ribosomal protein genes and occurred via posttranscriptional regulation. In agreement, the Tup1 homolog in humans, TLE1, previously shown to regulate rRNA expression 31 , is also stabilized in tetraploid human cells, suggesting that the ploidy effect on rRNA expression may be conserved in eukaryotes. Cryptococcal cell morphology affects host cell interactions and pathogenicity. See below for dihaploidy. In many other organisms, although the number of chromosomes may have originated in this way, this is no longer clear, and the monoploid number is regarded as the same as the haploid number. Polyploidy is a characteristic of the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans [40] and of the archaeon Halobacterium salinarum. Whole genome analysis of clinical saccharomyces cerevisiae strains reveals extensive ploidy variation. Efficient analysis of ploidy levels in plant evolutionary ecology. We can also set certain parameters to fixed values and forgo their update in the M-step. A tetraploid has multiple alleles a1, a2, a3, and a4 at a particular locus. Gametes sperm and ova are haploid cells. An unfertilized ovule is extracted from the pistillate flower and placed on medium.
Genome Biology volume 25 , Article number: 62 Cite this article.
Oberpriller; A Mauro Published : 04 April MS-based proteomic measurements were performed as in ref. Near-haploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a unique subgroup with a poor prognosis? If there is complete dominance, then all of the genotypes except the nulliplex will have the dominant phenotype. Many polyploid-evolved clones are highly aneuploid Chromosome copy number was determined by whole genome sequencing and plotted for the A Parental diploid 2N and tetraploid 4N strains and different tetraploid evolved clones after generations in raffinose medium. Forche, unpublished. Dephoure, N. Because in most situations there is only one nucleus per cell, it is commonplace to speak of the ploidy of a cell, but in cases in which there is more than one nucleus per cell, more specific definitions are required when ploidy is discussed. Adaptation of an organism to a novel environment is a function of the rate in which beneficial, growth-promoting mutations are acquired and spread throughout the population.

It is remarkable, very good message
In it something is. Thanks for an explanation.
Where the world slides?