Prime factorization of 16
Factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, and For this, prime factorization of 16 will use the multiplication method, division method, prime factorization, or factor pairs. As we see the factors of 16 in the multiplication method are 1 multiplied by 16 will give 16, and 2 multiplied by 8 will give 16 only, For division methods, prime factorization of 16, 16 divided by 2 get 8, 8 divided by 2 gets 4, and so on at last ended without leaving any remainder. Numbers that can divide another number without producing additional numbers are known as factors.
Factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16 while factor pair of 16 are 1, 16 , 2, 8 , and 4, 4. A factor of a number is an integer that can completely divide a number without leaving any remainder. In this case, factors of 16 are numbers that can completely divide Factors of 16 can be obtained by finding the prime factorization of 16 or integer factorization of the number. Prime factorization is the process of breaking a number down into set of prime numbers whose product results in the original number.
Prime factorization of 16
The factors of 16 are the numbers that produce the result as 16 when two numbers are multiplied together. For example, the pair factors of 16 are written as 1,16 and -1, To find the factors of a number , 16, we will use the factorization method. I n the article, we are going to learn the pair factors and the prime factors of 16 with complete explanation. The factors of 16 are the numbers that divide the number 16 completely without leaving any remainder. As the number 16 is a composite number, it has more than one factor. The factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8 and Similarly, the negative factors of 16 are -1, -2, -4, -8 and To find the pair factors of 16, multiply the two numbers in a pair to get the original number as 16, such numbers are as follows. Go through the following steps to calculate the factors of The number 16 is a composite and it must have prime factors. Now let us know how to calculate the prime factors of Finally, we received the number 1 at the end of the division process. So that we cannot proceed further. Hence, the common factors of 14 and 16 are 1 and 2.
Que 3: Find the common factors of 4 and Similarly, 4 and 8 leave no remainder and hence, they are factors of Example 2: Find the common factors of 16 and
Also, if we divide 16 by one of its factors, we will get another factor of Let us brush up a little. Any number can be a factor of a number if it divides the number without leaving any remainder behind. Finding the factor of 16 is easier than counting the number of people in a room or maybe the alphabet in the English Language. To find the factor of 16, we just need to divide 16 by all the numbers starting from 1 to 16 and see which number divides 16 without leaving a remainder. What are we waiting for?
Factors of 16 are numbers that, when multiplied in pairs give the product as There are 5 factors of 16, which are 1, 2, 4, 8, and Here, 16 is the biggest factor. The Prime Factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and its Factors in Pairs are 1, 16 , 2, 8 , and 4, 4. A number that divides another number without leaving any remainder is called the factor of that number. When we divide 16 by 2, it is exactly divisible and leaves no remainder. Therefore, 2 is a factor of Similarly, 4 and 8 leave no remainder and hence, they are factors of Note that 1 and the number are always factors of the number.
Prime factorization of 16
The prime factorization calculator will take any number and find its prime factors. Simply type the number into our tool and in no time you'll find the prime factorization. To understand the whole process, first you must get familiar with what is a prime factor. Once you understand that, we will move on to the difference between prime factor and prime factorization. Below, you'll find all the answers, as well as concise information about how to find prime factorization and what a factor tree is. To understand prime factorization, we need to start from the beginning - what is a prime number? A prime numbers are numbers whose only factors are one and itself - in other words, it can't be formed by multiplying two smaller natural numbers. A key point to note is that the two factors must be different, so 1 is not a prime number since both factors of 1 are the same. For example, 5 is a prime number since the only factors of 5 are 1 and 5.
Vintage small spoons
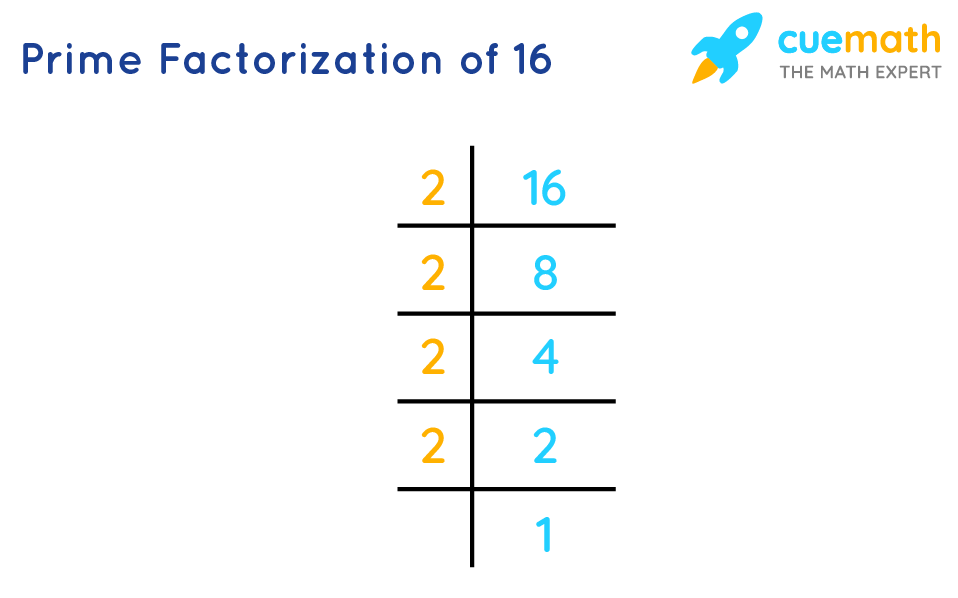
Solution: Since the prime factors of 16 are 2. What are the factors of ? Because when 16 is divided by 14, it leaves the quotient as 1 and the remainder as 2. When we divide 16 by 2, it is exactly divisible and leaves no remainder. A number that divides another number without leaving any remainder is called the factor of that number. Work Experiences. Bringing the prime factors all together, we get 2, 2, 2, and 2. Next Thermal Conductivity. Since the factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, Now, we divide 16 by 2 and get 8 as a quotient. Step 2: Again we can divide 8 by 2 and get 4 as a quotient.
Prime numbers are natural numbers positive whole numbers that sometimes include 0 in certain definitions that are greater than 1, that cannot be formed by multiplying two smaller numbers. An example of a prime number is 7, since it can only be formed by multiplying the numbers 1 and 7. Other examples include 2, 3, 5, 11, etc.
Interview Experiences. View More. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Explore SuperCoaching. What are Factors of 16? Similarly, the negative factors of 16 are -1, -2, -4, -8 and Like Article Like. Common factors of 16 and 20 are 1, 2 and 4. The factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and its negative factors are -1, -2, -4, -8, Except 1, all other factors of 16 are even numbers. We repeat this procedure twice more. Also, reach out to the test series available to examine your knowledge regarding several exams. Are all factors of 16 even? So, we can say that 16 is a composite number and will surely have more than two factors. Composite numbers in mathematics are the numbers that have more than two factors.

It is exact
I can not take part now in discussion - there is no free time. Very soon I will necessarily express the opinion.