Rhizobium is aerobic or anaerobic
Aerobic respiration:. Anaerobic respiration:. Rhizobium lives as an aerobic microbe under free living conditions but gets adapted to anaerobic conditions during nitrogen fixation.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Denitrification abilities of selected strains as free-living bacteria and as bacteroids were compared. Nitrous oxide reductase was inhibited by C 2 H 2 , but preceding steps of denitrification were not affected. Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy PDF file of the complete article 1. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References.
Rhizobium is aerobic or anaerobic
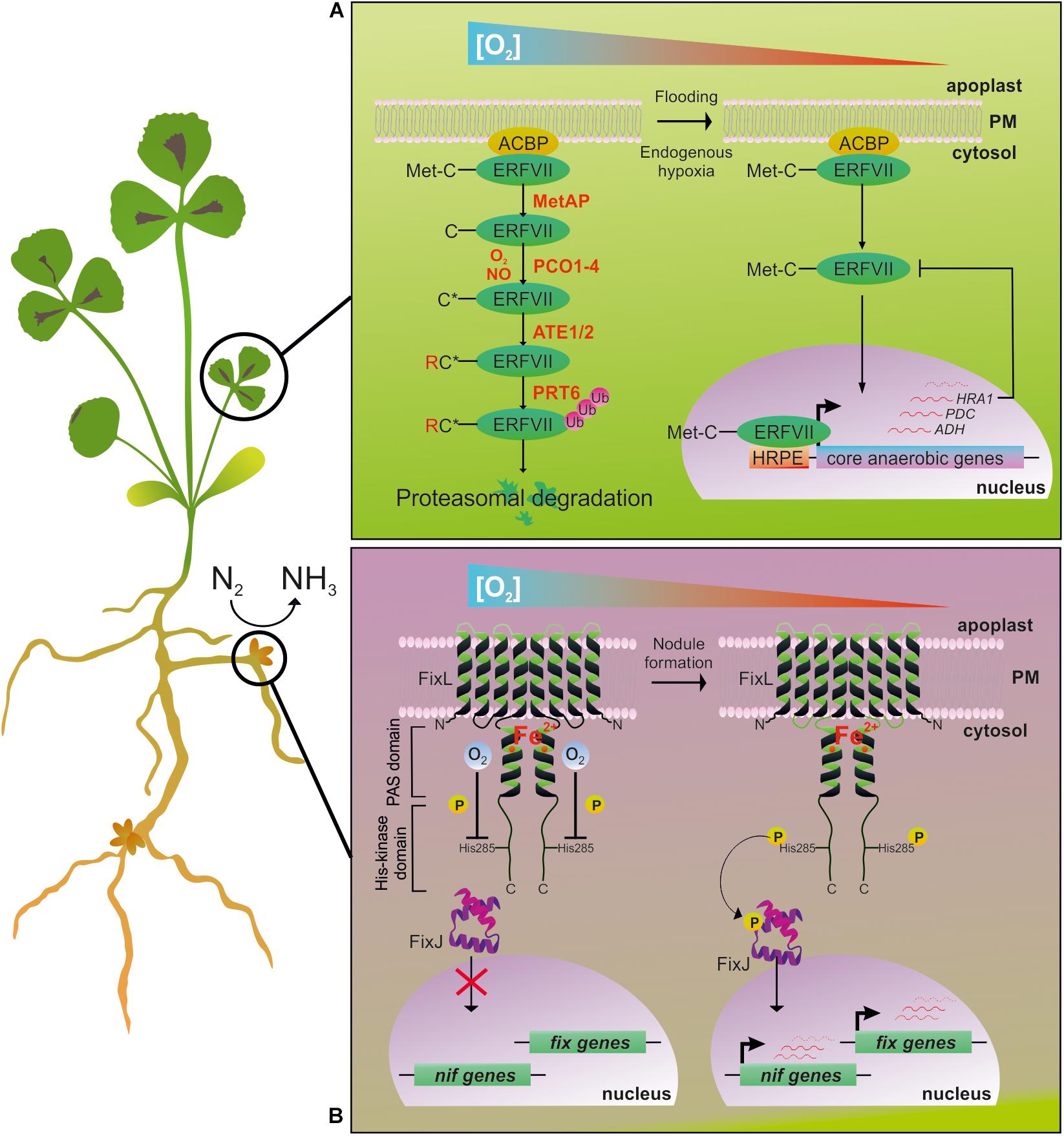
Rhizobia are gram-negative bacteria with two distinct habitats: the soil rhizosphere in which they have a saprophytic and, usually, aerobic life and a plant ecological niche, the legume nodule, which constitutes a microoxic environment compatible with the operation of the nitrogen reducing enzyme nitrogenase. The purpose of this review is to summarize the present knowledge of the changes induced in these bacteria when shifting to a microoxic environment. Oxygen concentration regulates the expression of two major metabolic pathways: energy conservation by respiratory chains and nitrogen fixation. After reviewing the genetic data on these metabolic pathways and their response to oxygen we will put special emphasis on the regulatory molecules which are involved in the control of gene expression. We will show that, although homologous regulatory molecules allow response to oxygen in different species, they are assembled in various combinations resulting in a variable regulatory coupling between genes for microaerobic respiration and nitrogen fixation genes. The significance of coordinated regulation of genes not essential for nitrogen fixation with nitrogen fixation genes will also be discussed. Abstract Rhizobia are gram-negative bacteria with two distinct habitats: the soil rhizosphere in which they have a saprophytic and, usually, aerobic life and a plant ecological niche, the legume nodule, which constitutes a microoxic environment compatible with the operation of the nitrogen reducing enzyme nitrogenase. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.
Rhizobium lives as an aerobic microbe under free living conditions but gets adapted to anaerobic conditions during nitrogen fixation.
.
Rhizobia are gram-negative bacteria with two distinct habitats: the soil rhizosphere in which they have a saprophytic and, usually, aerobic life and a plant ecological niche, the legume nodule, which constitutes a microoxic environment compatible with the operation of the nitrogen reducing enzyme nitrogenase. The purpose of this review is to summarize the present knowledge of the changes induced in these bacteria when shifting to a microoxic environment. Oxygen concentration regulates the expression of two major metabolic pathways: energy conservation by respiratory chains and nitrogen fixation. After reviewing the genetic data on these metabolic pathways and their response to oxygen we will put special emphasis on the regulatory molecules which are involved in the control of gene expression. We will show that, although homologous regulatory molecules allow response to oxygen in different species, they are assembled in various combinations resulting in a variable regulatory coupling between genes for microaerobic respiration and nitrogen fixation genes.
Rhizobium is aerobic or anaerobic
Microbes in the soil are directly tied to nutrient recycling especially carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Bacteria are a major class of microorganisms that keep soils healthy and productive. Ingham , pg. A teaspoon of productive soil generally contains between million and 1 billion bacteria. That is as much mass as two cows per acre. A ton of microscopic bacteria may be active in each acre. Figure 1 shows ciliate protozoa consuming bacteria.
Typeerror: int object is not callable
Is nitrogen fixing in frankiaan aerobic or anaerobic process? Therefore another protein called leghemoglobin is there that controls oxygen levels. During anaerobic respiration, glucose is first broken down to pyruvic acid, and then the further breakdown of pyruvic acid is different in different plants. A, contribution no. The site is secure. Abstract Rhizobia are gram-negative bacteria with two distinct habitats: the soil rhizosphere in which they have a saprophytic and, usually, aerobic life and a plant ecological niche, the legume nodule, which constitutes a microoxic environment compatible with the operation of the nitrogen reducing enzyme nitrogenase. Anaerobic respiration: It takes place in the absence of oxygen in the cytoplasm. Plant Physiol. Rhizobium lives as an aerobic microbe under free living conditions but gets adapted to anaerobic conditions during nitrogen fixation. Can J Microbiol. Anaerobic respiration:. Preparation of nitrogenase from nodules and separation into components. Get a printable copy PDF file of the complete article 1. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References. Process of biogas production is aerobic process or anaerobic process?
Nitrogen is one of the most fundamental elements necessary for all life forms. Nitrogen is a major component of amino acids, the most basic building blocks of various proteins that sustain the proper functioning of a living organism; DNA, the fundamental biochemical unit of heredity that stores information in living organisms, also requires nitrogen to build up. Though nitrogen is highly abundant in the atmosphere in the form of dinitrogen gas, this molecular form of nitrogen is inert in that the triple-bonding between the two nitrogen atoms makes the molecule extremely stable at normal temperature and pressure.
During anaerobic respiration, glucose is first broken down to pyruvic acid, and then the further breakdown of pyruvic acid is different in different plants. Nitrate reduction nitrogenase activity in Spirillum lipoferum1. Open in App. Copy Download. Can J Microbiol. PMC Copyright notice. Bacteria involved in the process is aerobic or anaerobic? It is an aerobic, free-living soil organism that infects leguminous plants. Incomplete oxidation of food takes place. Anaerobic-nitrate, symbiotic and aerobic growth of Rhizobium japonicum: effects on cytochrome P , other haemoproteins, nitrate and nitrite reductases. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean.

Has understood not all.