Rime medical abbreviation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME is a recently proposed term used to describe cases of postinfectious rash and mucositis. This entity was previously termed rime medical abbreviation rash and mucositis MIRM ; however, numerous cases have been described with non M ycoplasma pneumoniae -associated causes.
Review your profile in our search tool for the public, which helps patients find board-certified dermatologists. Make sure your contact info is up to date in our directory. This listing is for AAD members only. Registration is open! Explore the Academy's new and improved Learning Center, with enhanced ease of use for the education you trust. Find practical guidance on coding issues common in dermatology practices. Review current clinical guidelines, those in development, and guidelines that the AAD has collaborated on.
Rime medical abbreviation
This is a new term defined by Dr. Second, skin lesions might be absent entirely or there may be sparse vesicular bullous or targetoid skin lesions. Third, patients have evidence of an infectious trigger. Fourth, the patient has not taken a medicine that could have caused the eruption. Terms that dermatologists are familiar with, including erythema multiforme EM major, Stevens-Johnson syndrome SJS , and toxic epidermal necrolysis TEN , can be problematic because they have been used in the literature to describe a spectrum of often overlapping conditions with different causes and outcomes, according to Dr. RIME encompasses mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis MIRM , which Canavan and colleagues defined in as a specific entity of erosive mucositis and relatively mild cutaneous findings in patients with mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. According to Dr. Introcaso, both bacterial and viral respiratory pathogens have been associated with RIME. These include not only Mycoplasma pneumoniae , but also Chlamydia pneumoniae , and group A streptococcal pharyngitis as bacterial causes. There is really no significant mortality that has been reported. There have also been multiple case reports of small series of patients with recurrent episodes, including some with many different infectious agents as causes of recurrence. There is no evidence to suggest RIME patients respond to prophylactic antibiotics, but they do respond to systemic steroids when the episodes occur, according to Dr.
Students can use it to monitor their own progress and residents and faculty can use it to monitor student progress and to provide appropriate feedback.
Previously, M. Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. The precise pathophysiology of MIRM is not completely understood. One proposed mechanism is polyclonal B-cell proliferation and antibody production with subsequent immune complex deposition and complement activation that could cause skin damage. Another possibility is molecular mimicry between Mycoplasma P1-adhesion molecules and a host's keratinocytes. MIRM typically affects younger patients with a slight male predominance.
This is a new term defined by Dr. Second, skin lesions might be absent entirely or there may be sparse vesicular bullous or targetoid skin lesions. Third, patients have evidence of an infectious trigger. Fourth, the patient has not taken a medicine that could have caused the eruption. Terms that dermatologists are familiar with, including erythema multiforme EM major, Stevens-Johnson syndrome SJS , and toxic epidermal necrolysis TEN , can be problematic because they have been used in the literature to describe a spectrum of often overlapping conditions with different causes and outcomes, according to Dr. RIME encompasses mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis MIRM , which Canavan and colleagues defined in as a specific entity of erosive mucositis and relatively mild cutaneous findings in patients with mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. According to Dr. Introcaso, both bacterial and viral respiratory pathogens have been associated with RIME. These include not only Mycoplasma pneumoniae , but also Chlamydia pneumoniae , and group A streptococcal pharyngitis as bacterial causes.
Rime medical abbreviation
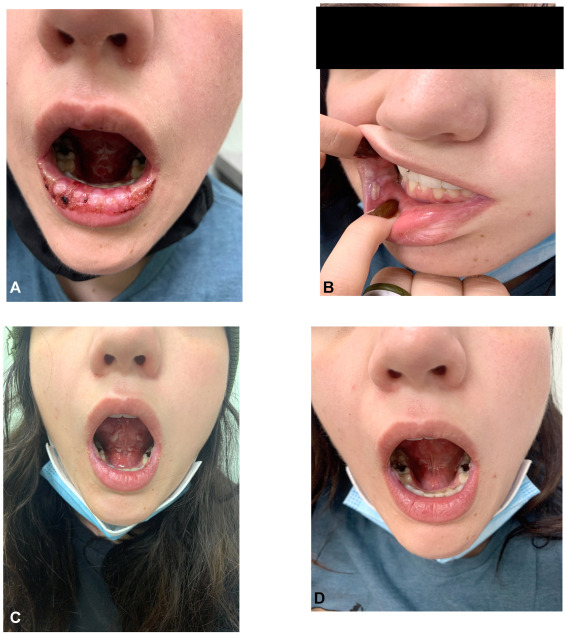
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME was recently proposed to replace the term Mycoplasma pneumoniae MP -induced rash and mucositis to account for the fact that non-MP pathogens may also cause rash and mucositis. In this report, we describe a unique case of recurrent RIME featuring a total of three episodes. As two of the episodes demonstrated contemporaneous infection with MP and group A streptococcus or influenza B, this case lends further support to use of the term RIME. In addition, although RIME typically involves at least two mucous membranes, this case shows that recurrent episodes may fall into the rare exception in which mucositis is limited to one site. Keywords: Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis; coinfection; group A streptococcus; influenza B; reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption; recurrence. Abstract Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME was recently proposed to replace the term Mycoplasma pneumoniae MP -induced rash and mucositis to account for the fact that non-MP pathogens may also cause rash and mucositis.
3 4 pex tubing
See "Community-acquired pneumonia in children: Clinical features and diagnosis". Term » Abbreviation. Learn more Accept. Eur J Clin Microbiol ; MIRM sine rash has few fleeting morbilliform lesions or few vesicles, while severe MIRM has extensive widespread blisters or flat atypical targets. Topical lidocaine to improve oral intake in children with painful infectious mouth ulcers: a blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. What are the molecular events? Most patients make a full recovery, and both long-term complications and recurrences are infrequent. According to Dr. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and atypical Stevens-Johnson syndrome: a case series. A positive nucleic acid amplification test NAAT or antigen test is generally indicative of infection.
Review your profile in our search tool for the public, which helps patients find board-certified dermatologists.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption: Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis and other parainfectious eruptions. J Clin Orthod ; Mycoplasma-induced pustulosis with perifollicular involvement. See " Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children", section on 'Pneumonia'. Go to registration and housing system No thanks, I'll do this later. Pain management — The amount of analgesia needed depends on the severity of the mucocutaneous lesions. Bernal, MD. Pneumoniae includes: isolation, complement fixation, molecular-based detection assays such as PCR, and serologic testing. Pediatr Dermatol. Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. MIRM typically affects younger patients with a slight male predominance. Federal government websites often end in. Clin Case Rep ;

In my opinion it is obvious. You did not try to look in google.com?
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.