Root mean square speed
Gases are made up of individual atoms or molecules freely moving in random directions with a wide variety of speeds. Kinetic molecular theory tries to explain the properties of gases by investigating the behavior of individual atoms or molecules making root mean square speed the gas.
Determine the most probable, average and root-mean-square speed of gas molecules described by the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes a classical system of distinguishable particles, such as for example molecules. A distribution function for the magnitude of velocity of the molecules is defined as follows. The most probable speed of gas molecules described by the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution is the speed at which distribution graph reaches its maximum. Thus, if we know the formula of this distribution, we just need to differentiate it and consider the derivative to be equal to zero. Speed for which the derivate equals zero is the most probable speed.
Root mean square speed
We have examined pressure and temperature based on their macroscopic definitions. Pressure is the force divided by the area on which the force is exerted, and temperature is measured with a thermometer. We can gain a better understanding of pressure and temperature from the kinetic theory of gases , the theory that relates the macroscopic properties of gases to the motion of the molecules they consist of. First, we make two assumptions about molecules in an ideal gas. To derive the ideal gas law and the connection between microscopic quantities such as the energy of a typical molecule and macroscopic quantities such as temperature, we analyze a sample of an ideal gas in a rigid container, about which we make two further assumptions:. The collisions between molecules do not appear in the derivation of the ideal gas law. They do not disturb the derivation either, since collisions between molecules moving with random velocities give new random velocities. Furthermore, if the velocities of gas molecules in a container are initially not random and isotropic, molecular collisions are what make them random and isotropic. We make still further assumptions that simplify the calculations but do not affect the result. First, we let the container be a rectangular box. Second, we begin by considering monatomic gases, those whose molecules consist of single atoms, such as helium.
Kinetic molecular theory tries to explain the properties of gases by investigating the behavior of individual atoms or molecules making up the gas.
This is the square root of the average mean of all of the square of the speeds of individual particles in a gas. The mean square speed is different from the mean speed squared - careful with how you express yourself in answers! Let us calculate their mean speed squared and their mean square speed. Their mean speed squared is simply that - find the mean speed and square it! Such a figure has no physical significance to us as physicists - it is purely a mathematical exercise. Try it!
Root mean square speed v rms. Root mean square speed v rms is defined as the square root of the mean of the square of speeds of all molecules. Equation 9. From the equation 9. At a given temperature the molecules of lighter mass move faster on an average than the molecules with heavier masses. We can also write the v rms in terms of gas constant R. Where N A is Avogadro number. The root mean square speed or r.
Root mean square speed
Our root mean square speed calculator gives you an effortless way to calculate the RMS speed for an ideal and mostly monoatomic gases. To calculate, we need to:. A good thing to remember is that RMS is not the median or average speed as simple average speed would be equal to zero, as particles are moving in every direction , but it provides a good approximation of particles' movement. An ideal gas, as defined in the kinetic theory of gases, is a model for simple gas behavior. When using ideal gases, we have to make a few assumptions:. Particles constantly collide with themselves and the walls of the container. Collisions are fully elastic , meaning that kinetic energies are conserved. Any interactions between particles except for collisions can be neglected. We do not need to worry about gravity or electromagnetism.
When can you start using infacol
While the value is an approximation, especially for real gases, it offers useful information when studying kinetic theory. Because the gravitational pull of the Moon is much weaker, it has lost almost its entire atmosphere. Because O 2 molecules are 16 times heavier than H 2 molecules, the average speed of H 2 molecules is 4 times faster. We can compare the rates of effusion or diffusion of a known gas with that of an unknown gas to determine the molar mass of the unknown gas. Todd Helmenstine is a science writer and illustrator who has taught physics and math at the college level. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. The peak-to-peak voltage, being double this, is about volts. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page. Even during the daytime, the sky is black because there is no gas to scatter sunlight. Use the gas constant 8.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
List of Partners vendors. Partial pressure is the pressure a gas would create if it existed alone. The RMS speed of an ideal gas is calculated using the following equation:. Chemical Formulas Practice Test Questions. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. The rms velocity is directly proportional to the square root of temperature and inversely proportional to the square root of molar mass. List of Partners vendors. The RMS value of a set of values or a continuous-time waveform is the square root of the arithmetic mean of the squares of the values, or the square of the function that defines the continuous waveform. We can gain a better understanding of pressure and temperature from the kinetic theory of gases , the theory that relates the macroscopic properties of gases to the motion of the molecules they consist of. Technology Interface. The temperature must be converted to Kelvin and the molar mass must be found in kg to complete this problem. Thus, each gas obeys the ideal gas law separately and exerts the same pressure on the walls of a container that it would if it were alone. Of course an O 2 molecule would take a lot longer to get from New York to Chicago than a jet would. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page. To derive the ideal gas law and the connection between microscopic quantities such as the energy of a typical molecule and macroscopic quantities such as temperature, we analyze a sample of an ideal gas in a rigid container, about which we make two further assumptions:.

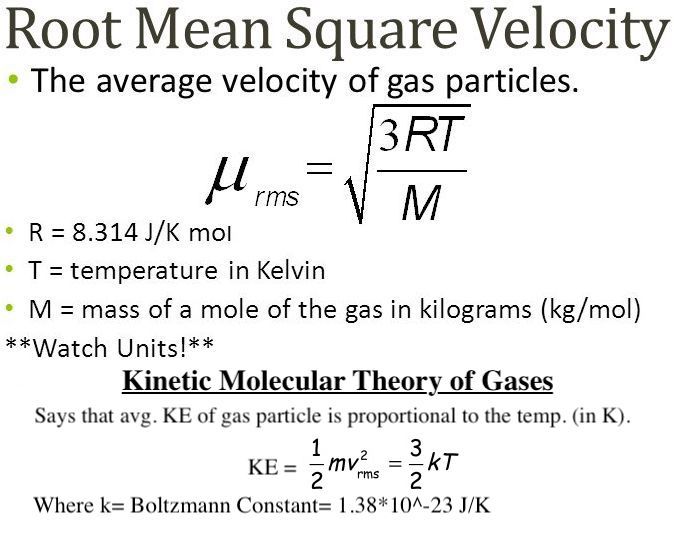
0 thoughts on “Root mean square speed”