Schwann cell
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, schwann cell, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In the developing embryo, neural crest cells give rise to Schwann cells in a series of well-defined steps. Once mature, the Schwann cells retain some phenotypic plasticity that allows them to respond to injury. Schwann cells develop from the neural crest in a well-defined sequence of events.
Schwann cell
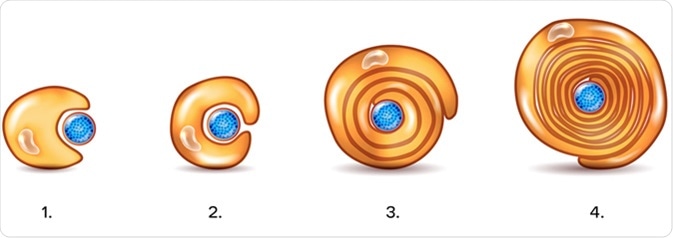
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system PNS. Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells , olfactory ensheathing cells , enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. The Schwann cell promoter is present in the downstream region of the human dystrophin gene that gives shortened transcript that are again synthesized in a tissue-specific manner. During the development of the PNS, the regulatory mechanisms of myelination are controlled by feedforward interaction of specific genes, influencing transcriptional cascades and shaping the morphology of the myelinated nerve fibers. Schwann cells are involved in many important aspects of peripheral nerve biology—the conduction of nervous impulses along axons , nerve development and regeneration , trophic support for neurons , production of the nerve extracellular matrix, modulation of neuromuscular synaptic activity, and presentation of antigens to T-lymphocytes. Schwann cells are a variety of glial cells that keep peripheral nerve fibres both myelinated and unmyelinated alive. In myelinated axons, Schwann cells form the myelin sheath. The sheath is not continuous. Individual myelinating Schwann cells cover about 1 mm of an axon [3] —equating to about Schwann cells along a 1-m length of the axon. The gaps between adjacent Schwann cells are called nodes of Ranvier. During peripheral nerve regeneration , 9-O-acetyl GD3 is expressed by Schwann cells. The action potential jumps from node to node, in a process called saltatory conduction , which can increase conduction velocity up to 10 times, without an increase in axonal diameter. In this sense, Schwann cells are the PNS's analogues of the central nervous system 's oligodendrocytes.
A dividing Schwann cell is seen double arrows.
.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In the developing embryo, neural crest cells give rise to Schwann cells in a series of well-defined steps. Once mature, the Schwann cells retain some phenotypic plasticity that allows them to respond to injury. Schwann cells develop from the neural crest in a well-defined sequence of events. This involves the formation of the Schwann cell precursor and immature Schwann cells, followed by the generation of the myelin and nonmyelin Remak cells of mature nerves. This review describes the signals that control the embryonic phase of this process and the organogenesis of peripheral nerves. We also discuss the phenotypic plasticity retained by mature Schwann cells, and explain why this unusual feature is central to the striking regenerative potential of the peripheral nervous system PNS. The myelin and nonmyelin Remak Schwann cells of adult nerves originate from the neural crest in well-defined developmental steps Fig.
Schwann cell
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Matthew Fallon ; Prasanna Tadi. Authors Matthew Fallon ; Prasanna Tadi 1. Schwann cells embryologically derive from the neural crest. They myelinate peripheral nerves and serve as the primary glial cells of the peripheral nervous system PNS , insulating and providing nutrients to axons.
زخرفة انجليزي
Comment on this article. This includes Schwann cell—autonomous effects, such as demyelination and proliferation, but also non-cell-autonomous effects, such as activation of the pathway, is sufficient to cause both a breakdown in the blood—nerve barrier and as robust an inflammatory response as seen following an injury. Genes Dev 15 : 66— Diabetes mellitus is associated with hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and impaired insulin signaling, which can damage microvasculature, leading to the common complication of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This can be seen in mice with genetic inactivation of neuregulin signaling, in which nerves follow a normal position and trajectory from the spinal cord toward their targets, although they lack Schwann cell precursors and are essentially composed only of axons Meyer and Birchmeier ; Morris et al. Salzer JL, Zalc B. Perhaps the most striking difference concerns survival regulation, because Schwann cell precursors are acutely dependent on the axon-associated survival signal neuregulin 1 type III, whereas immature Schwann cells survive in culture without addition of survival factors because of secretion of autocrine survival signals Dong et al. Keynes RJ. Gene profiling and bioinformatics analysis of Schwann cell embryonic development and myelination. Parts Soma Axon hillock. Neuregulin is expressed on axons and in embryonic DRG and motor neurons.
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system PNS. Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells , olfactory ensheathing cells , enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating.
Science : 82— On the other hand, the plasticity of myelin cells allows them to respond adaptively to injury by converting to cells that support regeneration. After longer periods, however, most Schwann cells without axonal contact in injured adult nerves die Hoke ; Sulaiman and Gordon Bunge; Martin E. P0- mice developed behavioral deficits around 2 weeks of age when mice began to show signs of slight trembling. Kettenmann H, Ransom BR , pp. Plexiform neurofibromas are often congenital, not hormone-responsive, and can undergo malignant transformation to MPNSTs. The myelin cells that previously formed flattened sheaths around axons, adopt an elongated bipolar morphology, allowing them to align to form a Schwann cell column named Bungner band inside each of the basal lamina tubes that formerly enclosed a myelin Schwann cell and its axon. Carroll SL. Changes in DNA synthesis rate in the Schwann cell lineage in vivo are correlated with the precursor—Schwann cell transition and myelination. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [ edit on Wikidata ]. The other component of the Schwann cell injury response is the appearance of novel phenotypes associated with neither Schwann cells in normal undisturbed nerves nor with immature Schwann cells.

It � is improbable!
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is and it is good idea. I support you.
Bravo, your idea it is very good