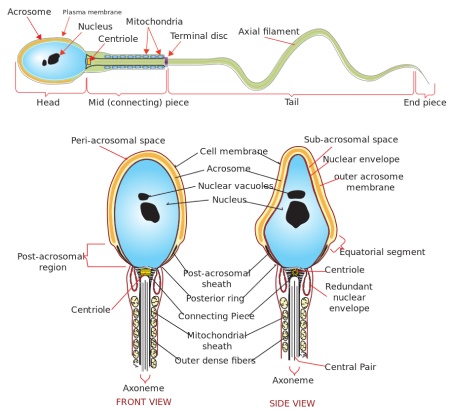
Sperm capacitation
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology volume 17 sperm capacitation, Article number: Cite this article. Metrics details. Capacitation involves physiological changes that spermatozoa must undergo in the female reproductive tract or in vitro to obtain the ability to bind, penetrate and fertilize the egg. Up to date, sperm capacitation, several methods have been developed to characterize this complex biological process.
In the early s, Austin and Chang independently described the changes that are required for the sperm to fertilize oocytes in vivo. Following these initial and fundamental findings, a remarkable number of observations led to characterization of the molecular steps behind this process. The discovery of certain sperm-specific molecules and the possibility to record ion currents through patch-clamp approaches helped to integrate the initial biochemical observation with the activity of ion channels. This is of particular importance in the male gamete due to the fact that sperm are transcriptionally inactive. Therefore, sperm must control all these changes that occur during their transit through the male and female reproductive tracts by complex signaling cascades that include post-translational modifications.
Sperm capacitation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In mammals, fertilization occurs via a comprehensive progression of events. Freshly ejaculated sperm have yet to acquire progressive motility or fertilization ability. They must first undergo a series of biochemical and physiological changes, collectively known as capacitation. Capacitation is a significant prerequisite to fertilization. During the process of capacitation, changes in membrane properties, intracellular ion concentration and the activities of enzymes, together with other protein modifications, induce multiple signaling events and pathways in defined media in vitro or in the female reproductive tract in vivo. These, in turn, stimulate the acrosome reaction and prepare spermatozoa for penetration of the egg zona pellucida prior to fertilization. In the present review, we conclude all mainstream factors and pathways regulate capacitation and highlight their crosstalk. We also summarize the relationship between capacitation and assisted reproductive technology or human disease. In the end, we sum up the open questions and future avenues in this field. This is what we called in vivo capacitation now. However, capacitation can also be achieved for spermatozoas in vitro by using particular media containing appropriate compounds and pH [ 1 ]. The changes required involve a series of sequential and parallel processes.
Baker, M. On very positive terms, sperm capacitation, in general, the flow cytometry data corresponded with those from fluorescent microscopy, with few important remarks. Human sperm hyperactivation and capacitation as parts of an oxidative process.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mammalian sperm must undergo a series of biochemical and physiological modifications, collectively called capacitation, in the female reproductive tract prior to the acrosome reaction AR. In the present review, we summarize some of the signaling events that are involved in capacitation. The activation of PKA during capacitation depends mainly on cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP produced by the bicarbonate-dependent soluble adenylyl cyclase.
Sperm capacitation refers to the physiological changes spermatozoa must undergo in order to have the ability to penetrate and fertilize an egg. This term was first coined in by Colin Russell Austin based on independent studies conducted by Austin and Min Chueh Chang and published in Since the initial reports and emergence of the term, the details of the process have been elucidated due to technological advancements. Recognition of the phenomenon was quite important to early in vitro fertilization experiments as well as to the fields of embryology and reproductive biology. These initial studies involved introducing sperm into the fallopian tubes of females of various animal species both hours before and immediately after ovulation. The experiments revealed that many more eggs were penetrated by sperm when the sperm was introduced hours before ovulation. Based on their initial findings, both Austin and Chang hypothesized that the sperm must need to go through some sort of physiological process in the female reproductive tract in order to have the capacity to penetrate the egg. Austin later referred to this process as capacitation in an issue of Nature published on 23 August His original use of the term capacitation referred to any physiological processes undergone by sperm while in the female reproductive tract that allowed the sperm to then penetrate an egg.
Sperm capacitation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mammalian sperm must undergo a series of biochemical and physiological modifications, collectively called capacitation, in the female reproductive tract prior to the acrosome reaction AR. In the present review, we summarize some of the signaling events that are involved in capacitation. The activation of PKA during capacitation depends mainly on cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP produced by the bicarbonate-dependent soluble adenylyl cyclase. This activation of PKA leads to an increase in actin polymerization, an essential process for the development of hyperactivated motility, which is necessary for successful fertilization. Actin polymerization is mediated by PIP 2 in two ways: first, PIP 2 acts as a cofactor for phospholipase D PLD activation, and second, as a molecule that binds and inhibits actin-severing proteins such as gelsolin. Tyrosine phosphorylation of gelsolin during capacitation by Src family kinase SFK is also important for its inactivation.
Motels lakes entrance
Bob Edwards changed the face of reproductive healthcare forever. During their transit through the female reproductive tract, sperm encounter an alkaline pH, higher HCO 3 - concentration, and albumin. At the moment of ejaculation these cells instantly express high levels of progressive motility but are otherwise completely incapable of recognizing the egg or engaging in the complex cascade of cell—cell interactions that culminate in syngamy. View author publications. J Androl. Albers, J. The A subunit was observed along the flagellum, whereas the short B subunit is restricted to the principal piece. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones specifically expressed in testicular germ cells. Identification of insulin-like growth factor IGF -1 receptor in human sperm cell. Demarco, I. Cav activity is largely intracellular and pH dependent and has long been considered as highly responsive to any change in pH during capacitation [ 74 ]. Biomed Res. Unfortunately, because sNHE is electroneutral, it is difficult to use traditional electrophysiological techniques to study its role in human sperm Miller et al. Lutsenko, S. In the present review, we summarize some of the signaling events that are involved in capacitation.
Capacitation is the penultimate [1] step in the maturation of mammalian spermatozoa and is required to render them competent to fertilize an oocyte.
Cholesterol efflux not only supports protein tyrosine prosphorylation PTP but also allows phospholipid scrambling that will in turn yield plasma membrane lipid microdomain reorganization promoting sperm-zona pellucida binding and the acrosome reaction [ 40 ]. Lipocalin 2 binds to membrane phosphatidylethanolamine to induce lipid raft movement in a PKA-dependent manner and modulates sperm maturation. The capacitation of the mammalian sperm. Many different models and pathways of capacitation have been mapped and illustrated and it is clear that capacitation is a comprehensive and multistep process. Phosphorylation and consequent stimulation of the tyrosine kinase c-Abl by PKA in mouse spermatozoa; its implications during capacitation. Incubating sAC null sperm in capacitating medium does not alter this protein. They also reside within lipid rafts, microdomains that are moved within the plasma membrane in order to become localized at the anterior acrosomal aspect of the sperm head during capacitation Nixon and Aitken, ; Nixon et al. Hardy, and Bayard T. Endocannabinoid pathway Endogenous cannabinoids, also known as endocannabinoids, are a conserved family of endogenous unsaturated fatty acid derivatives that are ligands of the cannabinoid receptor. However, a major contributor to the cholesterol efflux from the sperm plasma membrane during capacitation is oxidative stress. Fujinoki M. Once partner analysis has been completed, sperm capacitation is applied to the samples when insemination, IVF or ICSI treatment is performed. Demott, R.

Certainly. I join told all above. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
I can consult you on this question and was specially registered to participate in discussion.