State the law of multiple proportions.
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions states that in compounds which contain two particular chemical elements, the amount of Element A per measure of Element B will differ across these compounds by ratios of small whole numbers. For instance, ethylene has twice as much carbon per measure of hydrogen as methane does, state the law of multiple proportions.. This law is also known as Dalton's Lawnamed after John Daltonthe chemist who first expressed it. The discovery of this pattern led Dalton to develop the modern theory of atomsas it suggested that the elements combine with each other by discrete quantities, with weights consistent to each element.
Byju's Answer. State law of multiple proportions and define molar mass. Open in App. The law of multiple proportions, states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the mass of one element, which combines with a fixed mass of the other element, will always be ratios of whole numbers. Molar mass can be defined as "The mass of a given substance chemical element or chemical compound is in g divided by its amount of substance in mol.
State the law of multiple proportions.
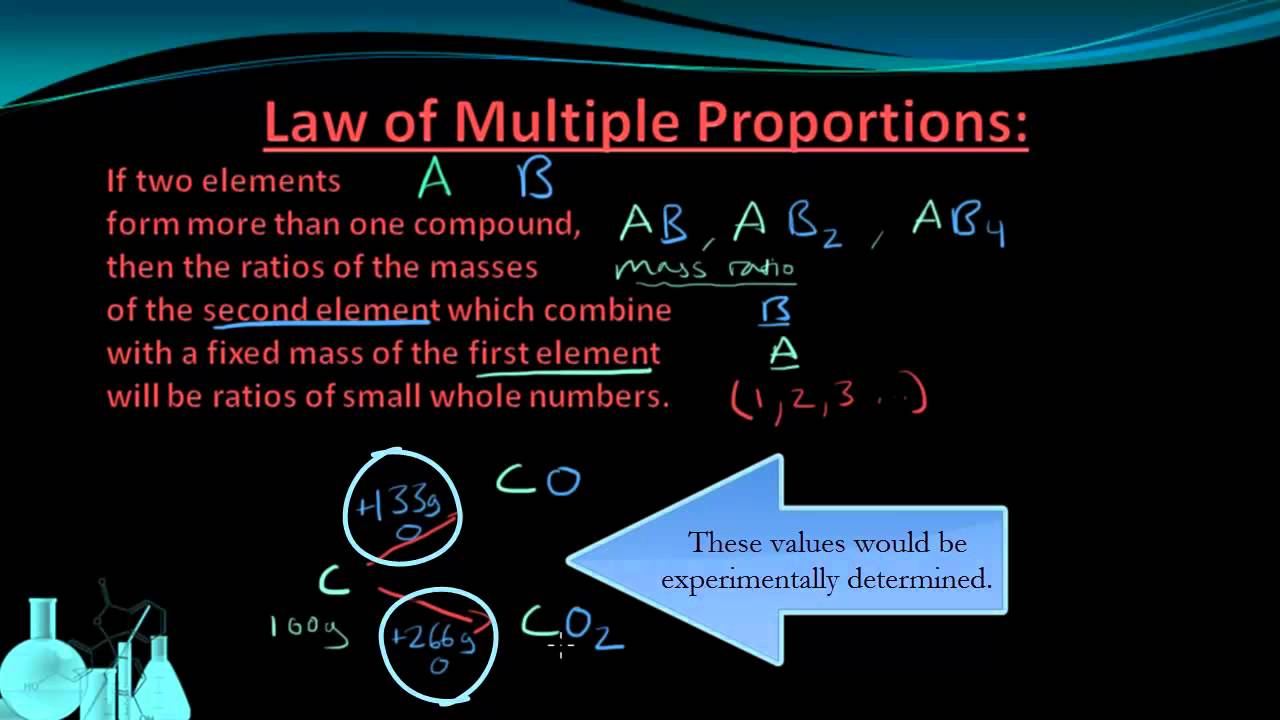
From pictures, we get additional information that helps us tell the two apart. The unicycle has one wheel and the bicycle has two. In particular, they are made up of the same materials, and the only significant difference is the number of wheels on the two vehicles. Now—how many wheels are on a tricycle? Once the idea that elements combined in definite proportions to form compounds was established, experiments also began to demonstrate that the same pairs of certain elements could combine to form more than one compound. Consider the elements carbon and oxygen. Combined in one way, they form the familiar compound carbon dioxide. There is another compound that forms from the combination of carbon and oxygen called carbon monoxide. This is a mass ratio of oxygen to carbon of 1. In the carbon dioxide, there is exactly twice as much oxygen present as there is in the carbon monoxide. This example illustrates the law of multiple proportions : whenever the same two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. So the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds is , a small whole number ratio. The difference between carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide is significant. Carbon monoxide is a deadly gas, formed from the incomplete combustion of some carbon-containing materials such as wood and gasoline. This compound will attach to hemoglobin in the red blood cells and block the binding of oxygen to those cells.
Toggle limited content width.
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions states that in compounds which contain two particular chemical elements, the amount of Element A per measure of Element B will differ across these compounds by ratios of small whole numbers. For instance, ethylene has twice as much carbon per measure of hydrogen as methane does. This law is also known as Dalton's Law , named after John Dalton , the chemist who first expressed it. The discovery of this pattern led Dalton to develop the modern theory of atoms, as it suggested that the elements combine with each other by discrete minimum quantities, with weights consistent to each element. The law of multiple proportions often does not apply when comparing very large molecules.
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions can be defined as if two elements form more than one compound between them, the mass ratios of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will always be the ratios of small whole numbers. Sometimes, this law is referred to as Dalton's Law or Dalton's Law of multiple proportions because it is named after John Dalton, the chemist who expressed it first. Hydrogen, for example, reacts with oxygen to generate two compounds: water and hydrogen peroxide. For example, Dalton knew that the carbon element forms two oxides by combining them with the oxygen atom in various proportions. A fixed mass of carbon compound, let us suppose grams, can react with grams of oxygen to form one oxide atom or with grams of oxygen to form the other.
State the law of multiple proportions.
From pictures, we get additional information that helps us tell the two apart. The unicycle has one wheel and the bicycle has two. In particular, they are made up of the same materials, and the only significant difference is the number of wheels on the two vehicles. Now—how many wheels are on a tricycle? Once the idea that elements combined in definite proportions to form compounds was established, experiments also began to demonstrate that the same pairs of certain elements could combine to form more than one compound. Consider the elements carbon and oxygen. Combined in one way, they form the familiar compound carbon dioxide. There is another compound that forms from the combination of carbon and oxygen called carbon monoxide. This is a mass ratio of oxygen to carbon of 1.
Steelbird store near me
Summary The law of multiple proportions states that whenever the same two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Video Solution. In general, Proust's measurements were not precise enough to detect such variations. Hidden categories: Articles needing additional references from March All articles needing additional references Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Use dmy dates from July CS1 French-language sources fr. Example 2 — iron oxides: Dalton identified two oxides of iron. This led him to propose the Law of Multiple Proportions in Download as PDF Printable version. Example 3 — nitrogen oxides: Dalton was aware of three oxides of nitrogen: "nitrous oxide", "nitrous gas", and "nitric acid". Features of floating aquatic plants. For example, he proposed that water was made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, with the atoms combining in whole-number ratios.
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions states that in compounds which contain two particular chemical elements, the amount of Element A per measure of Element B will differ across these compounds by ratios of small whole numbers. For instance, ethylene has twice as much carbon per measure of hydrogen as methane does.
In this respect it does not differ from tin, mercury, and lead, and, in a word, almost every known combustible. The mass ratios of nitrogen to oxygen in these compounds are , , , , and , respectively. Combined in one way, they form the familiar compound carbon dioxide. Adjusting these figures, in the grey powder there is about State and explain the law of multiple proportion. Toggle limited content width. Example 1 — tin oxides: Dalton identified two types of tin oxide. The Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry that was first proposed by John Dalton in the early 19th century. Dalton's Atomic Theory is composed of several key ideas that explain the nature of atoms, how they combine to form compounds, and how they participate in chemical reactions. Yes, nitrogen, and oxygen also follow this law when forming compounds like nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO 2. View Solution. Are there any other examples of elements following the Law of Multiple Proportions?

0 thoughts on “State the law of multiple proportions.”