Subjunctive spanishdict
The subjunctive el subjuntivo is one of three moods in Spanish. The other two Spanish moods are the indicative and the imperative.
The subjunctive el subjuntivo is a mood in Spanish grammar. It is a special verb from that indicates subjectivity or unreality. The Spanish subjunctive is used in simple sentences as well as in subordinate clauses after specific expressions. In subordinate clauses, the Spanish subjunctive usually follows que, although there are several other conjunctions and expressions that take the subjunctive. The subjunctive can signal uncertainty, doubt, possibility, desire, obligation or emotion. We also use the subjunctive after verbs of influence verbos de influencia like aconsejar, desear, mandar, necesitar, obligar , ordenar, suplicar, recomendar, querer, prohibir, etc.
Subjunctive spanishdict
The Spanish present subjunctive el presente de subjuntivo is used to talk about situations of doubt, desire, emotion, necessity, or uncertainty. Unlike the present indicative , the present subjunctive is generally subjective. For specifics on when to use the subjunctive instead of the indicative, see our article on subjunctive vs. To conjugate a verb in the present subjunctive, you must first remember what the present indicative yo form of the verb in question is. This is because the stem of present subjunctive verbs comes from the yo form of the present indicative. For many verbs, this will be the same as the infinitive stem, but for many others, such as verbs with spelling changes , stem-changing verbs , and irregular verbs , it will be different. Once you have the stem, you will add the present subjunctive ending that matches your subject. There are only two ending sets for the present subjunctive: one for -ar verbs and one for both -er and -ir verbs. In the table below are full present subjunctive conjugations for hablar , tener , and vivir. There are only six truly irregular verbs in the subjunctive.
Take a look at the following sets of examples and ask yourself why each one uses either the indicative or the subjunctive.
The subjunctive el subjuntivo is one of the three moods in Spanish, the other two being the indicative and the imperative. The subjunctive is used to express desires , doubts , wishes , conjectures , emotions , and possibilities. The subjunctive mood includes many of the same verb tenses as the indicative mood , including the perfect , the past , and the future , which is rarely used in modern Spanish, but good to know for literature. The subjunctive is often compared with the indicative. Check out our comparison here!
The Spanish present subjunctive el presente de subjuntivo is used to talk about situations of doubt, desire, emotion, necessity, or uncertainty. Unlike the present indicative , the present subjunctive is generally subjective. For specifics on when to use the subjunctive instead of the indicative, see our article on subjunctive vs. To conjugate a verb in the present subjunctive, you must first remember what the present indicative yo form of the verb in question is. This is because the stem of present subjunctive verbs comes from the yo form of the present indicative. For many verbs, this will be the same as the infinitive stem, but for many others, such as verbs with spelling changes , stem-changing verbs , and irregular verbs , it will be different. Once you have the stem, you will add the present subjunctive ending that matches your subject. There are only two ending sets for the present subjunctive: one for -ar verbs and one for both -er and -ir verbs. In the table below are full present subjunctive conjugations for hablar , tener , and vivir.
Subjunctive spanishdict
The Spanish subjunctive mood is crucial for delivering messages as simple as wishing a person a good day or giving advice. In short, this verb mood is fundamental to understanding and communicating effectively. The Spanish subjunctive mood refers to subjective and hypothetical situations. In simple words, el subjuntivo allows us to:. Unlike the indicative mood that focuses on certainty and reality, the subjunctive in Spanish is highly hypothetical. Check these examples:. I hope you have a good trip. I recommended them to watch this movie. Busco una casa que sea grande y accesible. Me da tristeza que ustedes no se lleven bien.
How to open bios msi
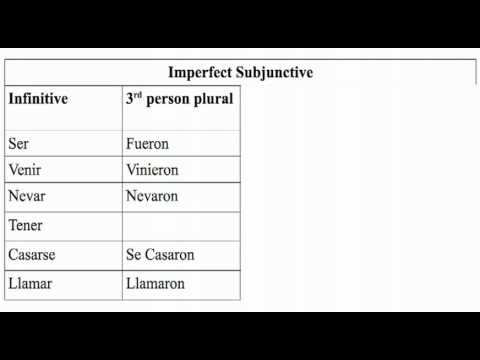
No te dije nada por miedo a que te enfadaras. Spanish Subjunctive Mood. The imperfect subjunctive el imperfecto de subjuntivo follows many of the same rules as the present subjunctive. When preceded by si if , the imperfect subjunctive is often used to talk about hypotheticals. Present Subjunctive. Examples Indicative or Subjunctive? Forgot Password? Review of Key Words and Phrases. Let's take a look at some of these verbs. Some students would rather the exams be oral exams. Learn more about recommendations and requests here. No matter how warmly I wrapped up, I got sick. No me mires como si estuviera loco.
This will help you navigate the common pitfalls, and know what common learner mistakes and perceptions to watch out for.
Emotions and Irregular Verbs. Learn more about impersonal expressions here. Comprehensive Review 2. Imperfect Subjunctive. To conjugate a verb in the present subjunctive, you must first remember what the present indicative yo form of the verb in question is. If I were queen, I would travel all over the world. Comprehensive Review 1. While this can be discouraging, fear not! Present tenses used in the subjunctive mood include the present subjunctive and the present perfect subjunctive. If Clauses. El viernes iremos al cine a menos que tengas una idea mejor. Take the test! Que yo sepa, Marta y Martina no son hermanas.

At all personal send today?
I well understand it. I can help with the question decision. Together we can come to a right answer.