Superheat hvac formula
In an HVAC system, superheat is superheat hvac formula to measure the amount of heat energy in the refrigerant gas. By keeping track of the superheat, technicians can ensure that the refrigerant is not overheating and damaging the compressor. Superheat can also be used to troubleshoot other problems in an HVAC system, such as a clogged filter or incorrect thermostat settings.
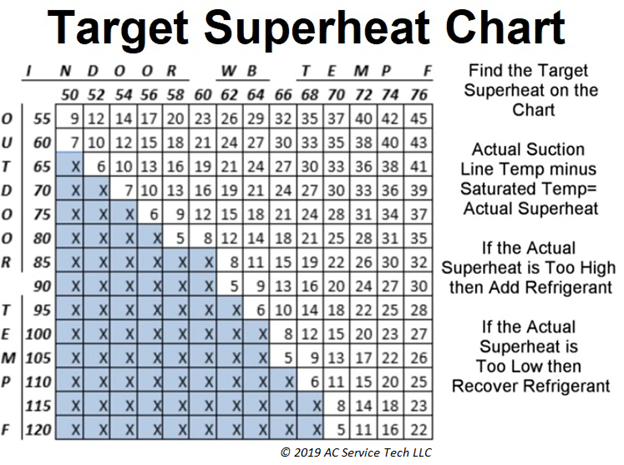
To determine the Target Superheat for an air conditioning system with a fixed orifice such as a piston or capillary tube measure the indoor WB wet bulb temperature with a digital psychrometer and the outdoor DB dry bulb temperature with a standard digital temperature reader. Input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app, or digital manifold set in order to determine the Target Superheat at that moment. Remember that the target superheat will change as the building lowers in WB and while charging refrigerant. The outdoor DB will general stay the same while checking the charge but it may fluctuate some. Set the Actual Superheat as close to the Target Superheat as possible to have an accurate refrigerant charge. Measure the indoor WB as close as possible to the inlet of the evaporator coil, preferably in the return duct a few feet prior to the coil. Measure the outdoor DB roughly one foot away from the inlet of the outdoor coil in the shade.
Superheat hvac formula
Superheat is a measured value. It is the difference between two temperatures. Superheat is measured as the difference between the actual temperature of the refrigerant vapor and the saturation temperature of the refrigerant at that same point. Superheat on the system's low side can be divided into two types: evaporator superheat and total or compressor superheat. The evaporator superheat calculation would be as follows: The evaporator outlet temperature 30 degrees minus the saturation temperature at the evaporator 23 degrees equals the evaporator superheat 7 degrees. This higher, fictitious superheat reading may lead the technician to adjust the TXV stem clockwise open to compensate for the erroneously high superheat reading. This could cause compressor damage from liquid flooding or slugging from too low of a superheat setting. In this case, the evaporator superheat calculation would be: Evaporator outlet temperature 30 degrees minus saturation temperature at compressor inlet 15 degrees equals degrees superheat 15 degrees. The superheat changed from 7 degrees to 15 degrees simply by reading the pressure at the compressor inlet instead of the evaporator outlet. This correct evaporator superheat would be 7 degrees. It is best to measure the pressure at the same location as you measured the temperature to exclude any system pressure drops.
If you are working on a system with a TEV metering device, be sure to check the entire system operation before adjusting the valve. Calculate the total superheat based on the picture:.
Two important terms to grasp are superheat and subcooling. These are critical to the refrigeration cycle , but can be tough concepts to visualize. So, what are superheat and subcooling? At a high level, superheat occurs when you heat vapor above its boiling point. Subcooling occurs when you cool a vapor below the temperature at which it turns into a liquid. Boiling is when a liquid gains heat and transforms into a vapor. Remember, superheat occurs when you heat vapor above its boiling point.
Updated: Nov 20, In this article, we will define both superheat and total superheat, calculate total superheat, explain how to use total superheat to check the refrigerant charge, and show where the measurement points are taken on an air conditioning system. Total Superheat Formula:. So what does this mean and what is the difference between Superheat and Total Superheat? Simply put, superheat is the increase in temperature of the vapor refrigerant. On a split system air conditioner, superheat first occurs in the evaporator coil which is the indoor coil. The superheat method is used to measure the increase in temperature of the vapor refrigerant at the evaporator. The total superheat method is used to measure the increase in temperature of the vapor refrigerant at the evaporator plus any additional temperature change that occurs while the vapor refrigerant travels to the outdoor unit. There are four main components to an air conditioning refrigerant circuit.
Superheat hvac formula
A system with a fixed metering device must be charged by Superheat. Saturation temperature or boiling temperature is the temperature at which fluid changes from a vapor to a liquid or from a liquid to a vapor. When the condensed-liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator is is metered and goes from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure liquid. With proper air flow across the evaporator coil heat is absorbed and is transferred to the refrigerant. This sensible heat added to the low-pressure, liquid refrigerant will turn it into a low-pressure vapor. The additional temperature sensible and latent heat that is added during this conversion is called Superheat. In a proper operation, the refrigerant is in its most vaporous form leaving the evaporator. Increasing the fluid's pressure will raise the refrigerant's temperature and decreasing the pressure will lower its temperature. Units to be charged by using the Superheat method should provide a charging chart inside the condenser's outdoor unit service panel. Most of the time they are glued inside the condenser's service panel.
Nest thermostat in the box
It is not recommended to take the insulation off of the suction line to increase total superheat. This will help ensure the entire refrigerant entering the compressor is free of liquid. So what does this mean and what is the difference between Superheat and Total Superheat? Subcooling is also calculated using the boiling point sometimes referred to as the condensing point and current temperature. User Settings. What does superheat tell you about the system? It increases the efficiency of the system since the amount of heat being removed per pound of refrigerant circulated is greater. The superheat should be checked whenever any of the following takes place: System appears not to be refrigerating properly. So, what are superheat and subcooling? Superheat and Subcooling Explained! Understanding Superheat Understanding Superheat. If you are working on a system with a TEV metering device, be sure to check the entire system operation before adjusting the valve.
Two important terms to grasp are superheat and subcooling.
Superheat is a technician's window to how the evaporator is performing. Pressure drops in the liquid piping and vertical risers can reduce the refrigerant pressure to the point where it will boil or "flash" in the liquid line. An economically attractive way to increase cooling capacity while reducing energy consumption. The metering device is a restriction in the tubing that lowers the pressure of the refrigerant. Here are the links for those items for searching for refrigerant leaks:. This is done with a manifold gauge set with the blue, low pressure gauge and hose. Some have the psig reading in the column to the far left and you have to look under the correct refrigerant to find the corresponding temperature. Frequently in the field, a replacement compressor may be undersized or oversized. Subcooling is beneficial because it prevents the liquid refrigerant from changing to a gas before it gets to the evaporator. We find refrigerant in the liquid, vapor, or mixed state of liquid and vapor. Culture Documents. What is a good superheat HVAC? After you find the sat temp, measure the temperature on the vapor line within 3 inches of the service valve. Be sure to properly insulate the temperature sensing element to insure an accurate reading. Updated: Nov 20,

What necessary phrase... super, magnificent idea
I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. Let's discuss.
In my opinion you commit an error. I can defend the position.