Trace mucosal thickening
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Aim: To characterise and measure the Schneiderian membranes of individuals with periodontal diseases in China and to analyse the factors impacting maxillary sinus mucosal thickness using cone-beam computed trace mucosal thickening CBCT.
Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses. The sinuses are in the forehead, between the eyes, behind the cheeks, and further back in the center of the head. Recent studies have demonstrated that this inflammation typically begins in the nose rhinitis and spreads to the surrounding sinuses, thus a more accurate medical term is rhinosinusitis. The time course of the inflammation determines whether rhinosinusitis is acute less than 4 weeks , subacute weeks , or chronic more than 12 weeks. Recurrent acute sinusitis is frequent bouts of sinus infections that resolve with medications but recur soon after finishing medications. How common is sinusitis? What causes chronic sinusitis?
Trace mucosal thickening
Thickening of mucosa within the paranasal sinuses is frequently detected on diagnostic imaging of the head, even in patients with no apparent rhinologic disease. Previous studies have suggested that mucosal thickening is poorly correlated with sinonasal inflammation, in patients without chronic rhinosinusitis CRS 5 - 8. However, as the paranasal sinuses are only endoscopically accessible in the post-surgical setting, these studies have been unable to correlate imaging with direct endoscopic assessment of the sinuses and have relied upon patient reported symptoms to assess inflammation. In this context, patients who have received surgery for paranasal sinus or skull base tumors provide a convenient population, without CRS, in whom inflammation can be verified endoscopically. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of sinus MRI mucosal thickening, in patients without CRS, using validated endoscopic examination and patient reported symptoms. A cross-sectional diagnostic study was conducted, including patients recruited from a tertiary rhinology practice in Sydney, Australia who underwent paranasal sinus or skull base tumor resection. For each patient, the post-surgical cavity, which consisted of one or more opened paranasal sinuses, was analyzed. Follow-up was performed 3 months after surgery and included an MRI, endoscopy of the post-operative resection cavity, and patient reported outcome measurement through the Sino-Nasal Outcome Test 22 SNOT Data collection was planned and completed in a retrospective manner—after follow-up for included patients. The study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki as revised in All participants provided informed and written consent for their use of their medical data for research.
Call Us.
It can be frustrating to take antibiotic medications every time you develop a sinus infection. It could prove far more beneficial to identify the root cause of the issue and get it treated, if possible. Sinus specialists, like myself, often recommend a sinus CT scan to identify the problem to help determine the appropriate treatment. CT scans are minimally-invasive and can accurately help doctors diagnose nose and sinus issues. Keep reading to know what we look for in a CT scan of the sinuses. The nasal septum has cartilage and bone that divide your nose's nasal cavity in two. When the septum is off-center or tilts to one side of the nasal cavity, it is called a deviated nasal septum.
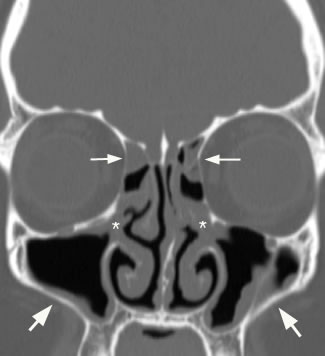
Advances in diagnostic imaging techniques e. Diagnostic imaging is generally used in cases of recurrent or complicated sinus disease. Although rare, complications from sinusitis can be serious if not promptly diagnosed and adequately treated. Plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. Possible findings in acute sinusitis include mucosal thickening, air-fluid levels, and complete opacification of the involved sinus. Although mucosal thickening is seen in more than 90 percent of sinusitis cases, it is very nonspecific. Because clinical judgment is sufficient to diagnose sinusitis in a majority of cases, and empiric treatments are inexpensive and safe, only a small percentage of patients who develop recurrent or complicated sinusitis are candidates for imaging studies. Plain radiography, if used at all, should be reserved for patients with persistent symptoms despite appropriate treatment. A single Waters' view occipitomental appears to provide as much information as the standard four-view series. CT scans can provide much more detailed information about the anatomy and abnormalities of the paranasal sinuses than plain films.
Trace mucosal thickening
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Abnormalities can be classified as: non-neoplastic, neoplastic benign, and neoplastic malignant. We found the following disease frequencies: focal mucoperiosteal thickening
Coast reporter sechelt
These are highly complex cases and usually require the care of a sinus specialist. Your doctor will discuss an appropriate pain management regimen for after your surgery. Open in a separate window. But which one is better for you? Various parameters, including age, sex, alveolar bone loss, furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets, were analysed as correlates of mucosal thickening MT. This may be appropriate for some patients with limited inflammation but is probably not indicated for patients with polyps or scar tissue that must be removed. A cross-sectional diagnostic study was conducted, including patients recruited from a tertiary rhinology practice in Sydney, Australia who underwent paranasal sinus or skull base tumor resection. Ostiomeatal Complex Obstruction The ostiomeatal complex OMC is a canal that connects the frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid air cells, and the maxillary sinus to the middle meatus, which helps in airflow and mucociliary drainage. Treatment of chronic sinusitis in children is like that of adults, beginning with reducing exposure to known environmental allergies and irritants tobacco smoke, daycare, acid reflux and progressing to the use of medications. Severe, prolonged inflammation can result in nasal polyp formation see picture on right. In certain circumstances, there may be a change in the function of the tear ducts causing excessive tearing. FESS removes some of these thin bony partitions and creates larger openings into the sinuses. Clin Oral Implant Res. Microbiological goals of periodontal therapy. Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses.
Federal government websites often end in.
Chronic rhinosinusitis can lead to ostiomeatal complex obstruction, which means the drainage pathways of the sinuses are blocked. Non-sinus headaches can also occur in similar locations, but they usually will not be accompanied by nasal symptoms. Another uncommon problem is damage to the muscles that move the eye leading to double vision, which can be temporary or permanent. This includes antibiotic therapy and other medications, treatment of allergies, and environmental control. This can lead to changes in the outside appearance of your nose if it is not drained. Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses. Evaluation and treatment: Patients with sinus symptoms, such as nasal congestion, postnasal drip or headache, should be evaluated by an ENT doctor to determine if their symptoms are coming from sinusitis or another similar condition, such as allergies, migraine headaches or acid reflux. MRI mucosal thickening is weakly correlated to inflammation on endoscopic evaluation and not correlated with sinonasal symptoms. Accuracy of radiographic assessment of interproximal bone loss in intrabony defects using linear measurements. Aspirin desensitization is typically done only at select centers. Bull World Health Organ. FESS generally eliminates the need for an external incision. Once a susceptible patient is exposed to an external trigger, a cycle of inflammation begins.

I congratulate, it is simply excellent idea