Transducin
Transducin mediates signal transduction in a classical G protein-coupled receptor GPCR phototransduction cascade. Interactions of transducin with the receptor and the effector molecules had been extensively investigated and are currently defined at the atomic level. Protein-protein interactions underlying this transducin are largely unknown, transducin.
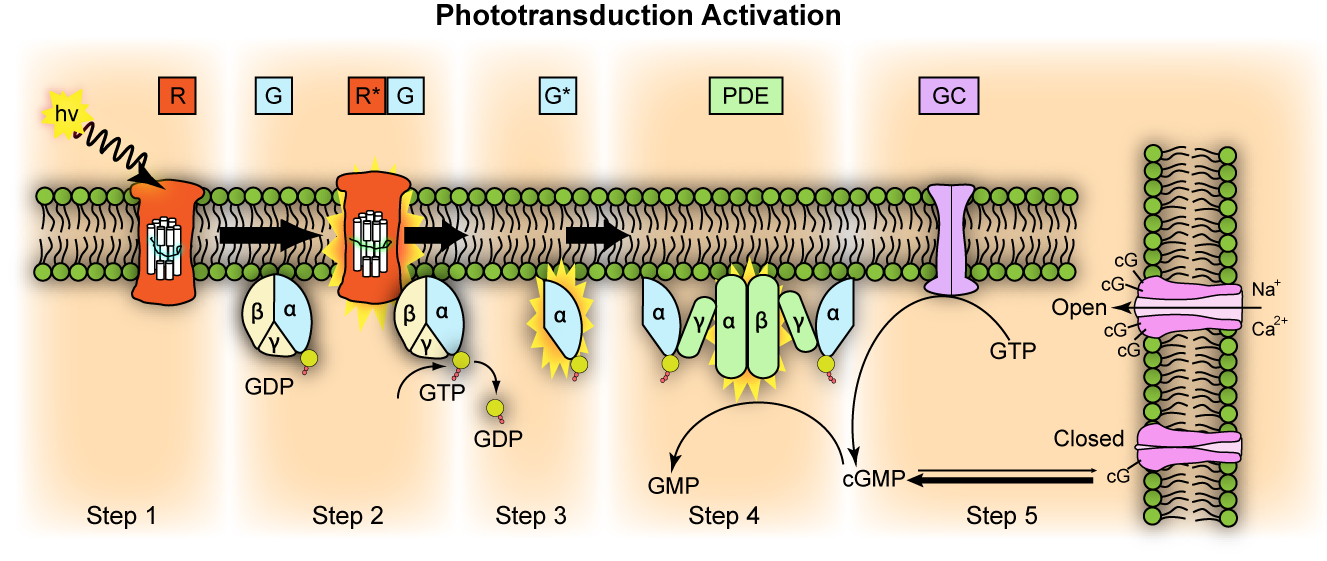
Transducin G t is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. Light leads to conformational changes in rhodopsin , which in turn leads to the activation of transducin. Transducin activates phosphodiesterase , which results in the breakdown of cyclic guanosine monophosphate cGMP. The intensity of the flash response is directly proportional to the number of transducin activated. Transducin is activated by metarhodopsin II , a conformational change in rhodopsin caused by the absorption of a photon by the rhodopsin moiety retinal. Isomerization causes a change in the opsin to become metarhodopsin II.
Transducin
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. To elucidate the determinants of G T coupling and activation, we obtained cryo-EM structures of a fully functional, light-activated Rho-G T complex in the presence and absence of a G protein-stabilizing nanobody. The structures illustrate how G T overcomes its low basal activity by engaging activated Rho in a conformation distinct from other GPCR-G protein complexes. Rho, the photoreceptor evolved for dim light vision in vertebrates, is a founding member of the G protein-coupled receptor GPCR superfamily that includes over members in humans Fredriksson et al. Rho is composed of the apoprotein opsin and a covalently bound ligand, cis retinal, which upon photon absorption, isomerizes to all-trans retinal thus activating Rho. The relatively high stability and abundance of Rho in vertebrate retinae Nickell et al. Crystallization efforts on Rho have yielded the first high-resolution structures of a GPCR in its inactive, apo and agonist-bound states Palczewski et al. However, the lack of a high-resolution complex containing Rho and its physiological signaling partner G T has hindered our understanding of the molecular basis for the remarkable signal amplification attained by this system. Furthermore, while recent advances in structural biology have started to yield high-resolution structures of GPCR-G protein complexes, including a 4. Here we describe cryo-EM structures of a fully functional and signaling-active Rho-G T complex, in the presence and absence of a newly engineered nanobody that does not interfere with G protein activation. The structures reveal how Rho specifically couples to and elicits a striking stimulation of its cognate signaling partner G T , and provide new insights into the mechanism of receptor-mediated G protein activation.
Otto-Bruc, A.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Our further analysis with this mechanism suggests that more effective PDE activation in disk membranes is highly dependent on the membrane environment. In the vertebrate photoreceptors, an enzymatic cascade, the phototransduction cascade, is responsible for generation of a light response 1 , 2.
Transducin G t is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. Light leads to conformational changes in rhodopsin , which in turn leads to the activation of transducin. Transducin activates phosphodiesterase , which results in the breakdown of cyclic guanosine monophosphate cGMP. The intensity of the flash response is directly proportional to the number of transducin activated. Transducin is activated by metarhodopsin II , a conformational change in rhodopsin caused by the absorption of a photon by the rhodopsin moiety retinal.
Transducin
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Most vertebrate animals depend on vision to navigate their environment and avoid predators. In the vertebrate eye, light is converted into electrical signals by a receptor protein known as rhodopsin, which spans the membranes of rod cells in the retina; the electrical signals are then processed in the brain to generate a mental image. Writing in Nature , Gruhl et al. Ernst, O. Article PubMed Google Scholar.
Shankar furniture
Annu Rev Physiol. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. The binding signal of PDE in Fig. Each determination was repeated for at least three pairs of wild-type and knock-out animals. Thus, retina represents an excellent opportunity to dissect the roles of Ric-8A. Localization of HRG4, a photoreceptor protein homologous to Unc, in ribbon synapse. Seven, A. In contrast, heterozygote mice showed no signs of degeneration, and their photoreceptor morphology was indistinguishable from that in the wild-type mice at all analyzed ages Figs. Structure of the visual signaling complex between transducin and phosphodiesterase 6. Karim, Z. Structures of the rhodopsin-transducin complex: insights into G-protein activation.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Neuron 27, — Dynein Kinesin Myosin Katanin. Maltose-neopentyl glycol MNG amphiphiles for solubilization, stabilization and crystallization of membrane proteins. The reason for this is not known. Yadav 1 Shivangi M. Bijveld, M. Neuron 28, — The G protein alpha chaperone Ric-8 as a potential therapeutic target. Together, these data provide a compelling argument in support of the need for stable transducin heterotrimer formation for proper outer segment localization. Given the high rate of transducin synthesis and transport in photoreceptors Frederick et al. Boularan, C. RGS expression rate-limits recovery of rod photoresponses. The buffer used was K-gluc buffer containing 0. Interactions of transducin with the receptor and the effector molecules had been extensively investigated and are currently defined at the atomic level.

This very valuable message