Trig proof solver
Each calculation option, trig proof solver, shown below, has sub-bullets that list the sequence of methods used in this calculator to solve for unknown angle and side values including Sum of Angles in a Triangle, Law of Sines and Law of Cosines.
The Pythagorean Theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation between the three sides of a right triangle. This is known as the Pythagorean equation, named after the ancient Greek thinker Pythagoras. This relationship is useful because if two sides of a right triangle are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to determine the length of the third side. Referencing the above diagram, if. It follows that the length of a and b can also be determined if the lengths of the other two sides are known using the following relationships:. The law of cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem that can be used to determine the length of any side of a triangle if the lengths and angles of the other two sides of the triangle are known.
Trig proof solver
.
Math is Fun at Solving Triangles.
.
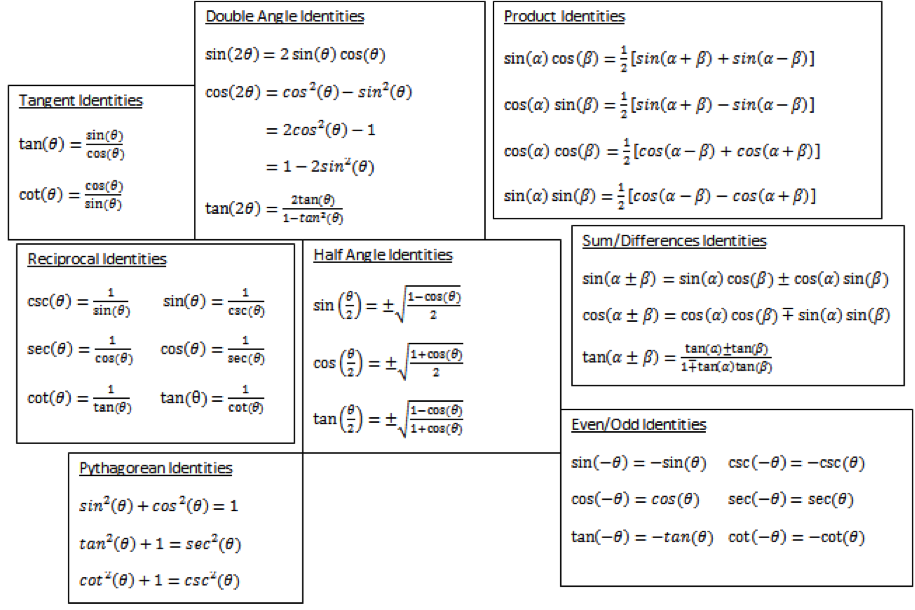
In this section, we will begin an examination of the fundamental trigonometric identities, including how we can verify them and how we can use them to simplify trigonometric expressions. Identities enable us to simplify complicated expressions. We can use algebraic techniques to simplify trigonometric expressions. Basic properties and formulas of algebra, such as the difference of squares formula and the perfect squares formula, will simplify the work involved with trigonometric expressions and equations. Consequently, any trigonometric identity can be written in many ways. To verify the trigonometric identities, we usually start with the more complicated side of the equation and essentially rewrite the expression until it has been transformed into the same expression as the other side of the equation. Sometimes we have to factor expressions, expand expressions, find common denominators, or use other algebraic strategies to obtain the desired result. We will begin with reviewing the fundamental identities already introduced in a previous section: the Pythagorean Identities , the Even-Odd or Negative Angle Identities , the Reciprocal Identities , and the Quotient Identities.
Trig proof solver
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user?
Walk of fame parking garage
There are numerous other proofs ranging from algebraic and geometric proofs to proofs using differentials, but the above are two of the simplest versions. It follows that the length of a and b can also be determined if the lengths of the other two sides are known using the following relationships:. Given the sizes of the 3 sides you can calculate the sizes of all 3 angles in the triangle. Last updated: February 6, If the angle between the other sides is a right angle, the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean equation. Referencing the above diagram, if. ASS Theorem. There are a multitude of proofs for the Pythagorean theorem, possibly even the greatest number of any mathematical theorem. In the figure above, there are two orientations of copies of right triangles used to form a smaller and larger square, labeled i and ii, that depict two algebraic proofs of the Pythagorean theorem. Triangle Image. In the second orientation shown in the figure, ii, the four copies of the same triangle are arranged such that they form an enclosed square with sides of length b - a, and area b - a 2.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:.
Referencing the above diagram, if. Weisstein, Eric W. There are numerous other proofs ranging from algebraic and geometric proofs to proofs using differentials, but the above are two of the simplest versions. Get a Widget for this Calculator. Therefore, specifying two angles of a tringle allows you to calculate the third angle only. Basic Calculator. In the second orientation shown in the figure, ii, the four copies of the same triangle are arranged such that they form an enclosed square with sides of length b - a, and area b - a 2. Follow CalculatorSoup:. In the first one, i, the four copies of the same triangle are arranged around a square with sides c. Significant Figures auto 3 4 5 6 7 8 9. You could also use the Sum of Angles Rule to find the final angle once you know 2 of them. Financial Fitness and Health Math Other. The four triangles with area ab 2 also form a larger square with sides of length c. The Pythagorean Theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation between the three sides of a right triangle.

I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. It is possible to discuss. Write here or in PM.