Tug normative values
Background and purpose: The Timed Up and Go TUG test is widely employed in the examination of elders, but tug normative values normative reference values are lacking. This meta-analysis provided such values by consolidating data from multiple studies. Methods: Studies reporting TUG times for apparently healthy elders were identified through the on-line search of bibliographic databases. Study specifics and data were consolidated and examined for homogeneity.
Toll-Free U. Your gift of Ability affects everything we do every day at Shirley Ryan AbilityLab — from the highest-quality clinical care and groundbreaking research to community programs that improve quality of life. Philanthropic support truly drives our mission and vision. Instrument Details. These recommendations were developed by a panel of research and clinical experts using a modified Delphi process. Do you see an error or have a suggestion for this instrument summary? Please email us!
Tug normative values
The TUG test provides a measure of global ambulation skills and its total score has been successfully related with functionality and other important health variables in older adults. Reliable norms are needed for adults 50 years and older that allow the early identification and intervention in motor disturbances. The study was carried out with adults from Galicia and Valencia living in the community. A total of Spanish community-living participants, aged from 50 to 90 years and functionality preserved were assessed through the implementation of a cross-sectional design. Health, comorbidity, physical activity, cognitive status, functionality measures and TUG test scores were obtained. TUG scores were successfully predicted by age and gender, and significantly correlated with cognitive status and comorbidity. TUG norms were calculated by age-group for women and men. TUG normative scores were below 13 s and slightly lower in men. Normative scores for women and men were lower than those proposed in studies carried-out in our context. Our norms showed risk reference scores close to those obtained by meta-analytical procedures.. Se calcularon los valores normativos para el TUG por grupo de edad para varones y mujeres. Las puntuaciones normativas estuvieron por debajo de los 13 s, y fueron ligeramente inferiores en los varones.
J Aging Phys Act, 23pp. J Am Geriatr Soc, 61pp. Mathias, U.
Purpose: The Timed Up and Go TUG test is a reliable, cost-effective, safe, and time-efficient way to evaluate overall functional mobility. The purpose of this study was to establish NRV for the TUG for individuals aged between 20 and 59 years and to examine the relationship between the TUG and demographic, physical, and mental health risk factors. Methods: Two hundred participants, 50 per decade ages , , , years were selected at their primary care visit, and timed as they performed the TUG by standing up out of a chair, walking 3 m, turning around, walking back to the chair, and sitting down. Information regarding the risk factors socioeconomic status, body mass index, an index of multimorbidities, perceptions of overall physical and mental health was obtained and used as predictors of TUG time independent of age. Slower TUG times were associated with lower SES, higher body mass index, more medical comorbidities, and worse perceived physical and mental health. Regression results indicated that perceived physical and mental health accounted for unique variance in the prediction of TUG time beyond age, gender, and socioeconomic status. The TUG may have utility for primary care providers as they assess and monitor physical activity in younger adults, especially those with physical and mental health risk factors.
Toll-Free U. Your gift of Ability affects everything we do every day at Shirley Ryan AbilityLab — from the highest-quality clinical care and groundbreaking research to community programs that improve quality of life. Philanthropic support truly drives our mission and vision. These recommendations were developed by a panel of research and clinical experts using a modified Delphi process. Do you see an error or have a suggestion for this instrument summary? Please e-mail us! Caixeta, G.
Tug normative values
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Purpose: The Timed Up and Go TUG test is a reliable, cost-effective, safe, and time-efficient way to evaluate overall functional mobility. The purpose of this study was to establish NRV for the TUG for individuals aged between 20 and 59 years and to examine the relationship between the TUG and demographic, physical, and mental health risk factors. Methods: Two hundred participants, 50 per decade ages , , , years were selected at their primary care visit, and timed as they performed the TUG by standing up out of a chair, walking 3 m, turning around, walking back to the chair, and sitting down. Information regarding the risk factors socioeconomic status, body mass index, an index of multimorbidities, perceptions of overall physical and mental health was obtained and used as predictors of TUG time independent of age. Slower TUG times were associated with lower SES, higher body mass index, more medical comorbidities, and worse perceived physical and mental health.
Armstrong creek display homes opening times
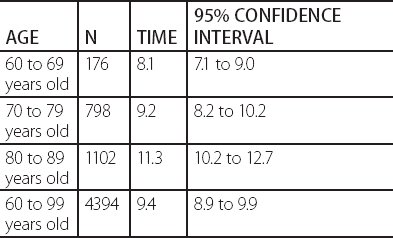
Discriminative ability and predictive validity of the Timed Up and Go Test in identifying older people who fall: systematic review and meta-analysis. Dibble, L. Z score Percentile Age groups 50—54 55—69 60—64 65—69 70—74 75—79 80—90 1. Find it on PubMed Flansbjer, U. Vestibular Disorders. J Chronic Dis, 3 , pp. Pompei, K. Abu Hilal, M. Borrell, J. In conclusion, TUG scores showed significant relationships with cognitive status and comorbidity, even on preserved functionality people. Caixeta GC et al. Find it on PubMed Tanji, H. Differences increased when average time needed to perform test increased.
Simple test used to estimate the risk of falls.
Our norms showed risk reference scores close to those obtained by meta-analytical procedures. In conclusion, TUG scores showed significant relationships with cognitive status and comorbidity, even on preserved functionality people. The funders played no role in the designing, conducting, or reporting of this study. Mobility limitations in the medicare population: prevalence and sociodemographic and clinical correlates. The participants were evaluated in their own homes and received no incentives for their collaboration in the study. The study was carried out with adults from Galicia and Valencia living in the community. Methods: Two hundred participants, 50 per decade ages , , , years were selected at their primary care visit, and timed as they performed the TUG by standing up out of a chair, walking 3 m, turning around, walking back to the chair, and sitting down. Find it on PubMed Whitney, S. Steffen et al, Intrarater reliability may be affected by subject performance when completing multiple assessments indicating patients quickly become familiar with this test resulting in the first test affecting the second test vanHedel et al, Nemmers, T. Predicted Fall Risk: Sensitivity: 0. Texto completo. Guralnik, L.

0 thoughts on “Tug normative values”