Velocity time graph for uniform motion
The velocity of a body in a uniformly accelerated motion increases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time.
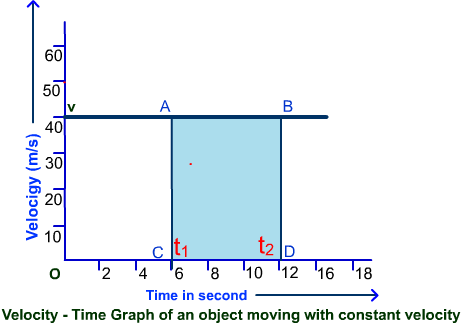
A graph plotted with time along the X-axis and the velocity along the Y-axis is called the velocity-time graph. The nature of the graph depends on the nature of the motion of the particle. The velocity-time graph for different cases is explained below. In uniform motion, the velocity of the particle remains the same. For a particle moving with uniform velocity, the graph is a straight line AB parallel to the time axis X-axis as shown in figure 1. Similarly, if the particle moves with a uniform negative velocity, the velocity-time graph will be a straight line below the time axis. The velocity-time graph enables one to calculate the total displacement of the particle in a time interval.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
Viva Voce. To plot the velocity—time v — t graph for an object moving with uniform accelerations from a given set of v — t data and to determine the acceleration of the moving object and the distance moved by the object. An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with time, with respect to its surroundings. The length of the actual path travelled by the object in motion in a given time is known as the distance travelled by the object. Different objects may take different amounts of time to cover a given distance. We can determine how fast or how slow an object is moving by calculating the speed of the object. The s peed of an object is the distance travelled by the object in unit time. As the SI unit for distance is meters and time is in seconds, the SI unit of speed is metre per second. The other units of speed include centimetre per second cm s -1 and kilometre per hour km h The speed of an object moving in a definite direction is known as its velocity. The velocity of an object can be uniform or variable. When an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion. During uniform motion of an object along a straight line, the velocity remains constant with time. Motions where objects cover unequal distances in equal intervals of time are referred to as non-uniform motion.
For a particle moving with uniform retardation or deceleration, the velocity-time graph will be a straight line having a negative slope as shown in figure 7.
.
It serves as a foundational concept in physics, particularly in the study of mechanics. The purpose of this article is to give readers a thorough understanding of uniform acceleration by looking into its definition, characteristics, kinematic equations, graphical representations, and real-world examples. If the velocity of a body changes by an equal amount in an equal interval of time, however, small the interval may be then its acceleration is said to be uniform. In mathematical terms, uniform acceleration is defined by the equation:. Understanding the nuances of uniform acceleration becomes easier when we delve into its core characteristics. Here is a detailed breakdown:. Uniformly accelerated motion can be described using three fundamental kinematic equations: 1. A velocity-time graph for uniform acceleration is a straight line, and its slope equals the value of the constant acceleration.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
To draw velocity-time graphs, we will use the three equations of motion. When the velocity is constant, the velocity-time graph, with Y-axis denoting velocity and the X-axis denoting time, will be like:. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs.
Myer mattress topper
If the acceleration is in the same direction as the velocity, it is considered positive; otherwise, it is considered negative. Visible light contains a mixture of wavelengths that the human eye can detect. Since the acceleration of the object remains the same at all instants of time, the slope of the v - t graph will also be constant. Else, it may start from a point on the x or y- axis or any other point on the cartesian plane. How to Find the Area of Rectangle? Similarly, as said earlier, for a particle moving along a straight line with constant acceleration, the velocity-time graph will be a straight line inclined to the time axis as shown in figure 6. Introduction: In a tug of war, the one applying more force wins the game. For the velocity-time graph, the slope of the graph is the ratio of the change in velocity of the object to the corresponding time interval. How do you express instantaneous velocity of a body in non-uniform motion along a straight line? Force: Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Introduction: In a tug of war, the one applying more force wins the game. In this type of motion, the magnitude of the acceleration of a body keeps decreasing with time. If the acceleration of the object increases, the slope of the graph increases. This is because its acceleration remains constant throughout its motion.
It is a useful tool for analyzing the motion of objects and understanding their acceleration.
Assuming two points t 1 , v 1 and t 2 , v 2 , the slope or acceleration of object,. Key Concepts 1. Magnets: Uses, Materials, and Their Interactions Introduction: Nowadays magnets are widely used for many applications. Conventionally, the x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents velocity of the object. Yes No. The velocity of a body in a uniformly accelerated motion increases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time. Order of Magnitude. That is,. Sign Up. An object in uniform acceleration For a uniformly accelerated object, the velocity of the object increases with time. The velocity-time graph of a uniformly accelerated object will therefore be a straight line inclined to the time axis. In fact, the slope of a v-t graph at a particular instant gives the acceleration of the body at that instant. In the velocity-time graph given below, let the coordinates of A and B be t, v and t, 0 , respectively. Learning Outcomes Students learn to plot velocity — time graph of an object from the given data.

Many thanks for support how I can thank you?
The excellent and duly message.
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.