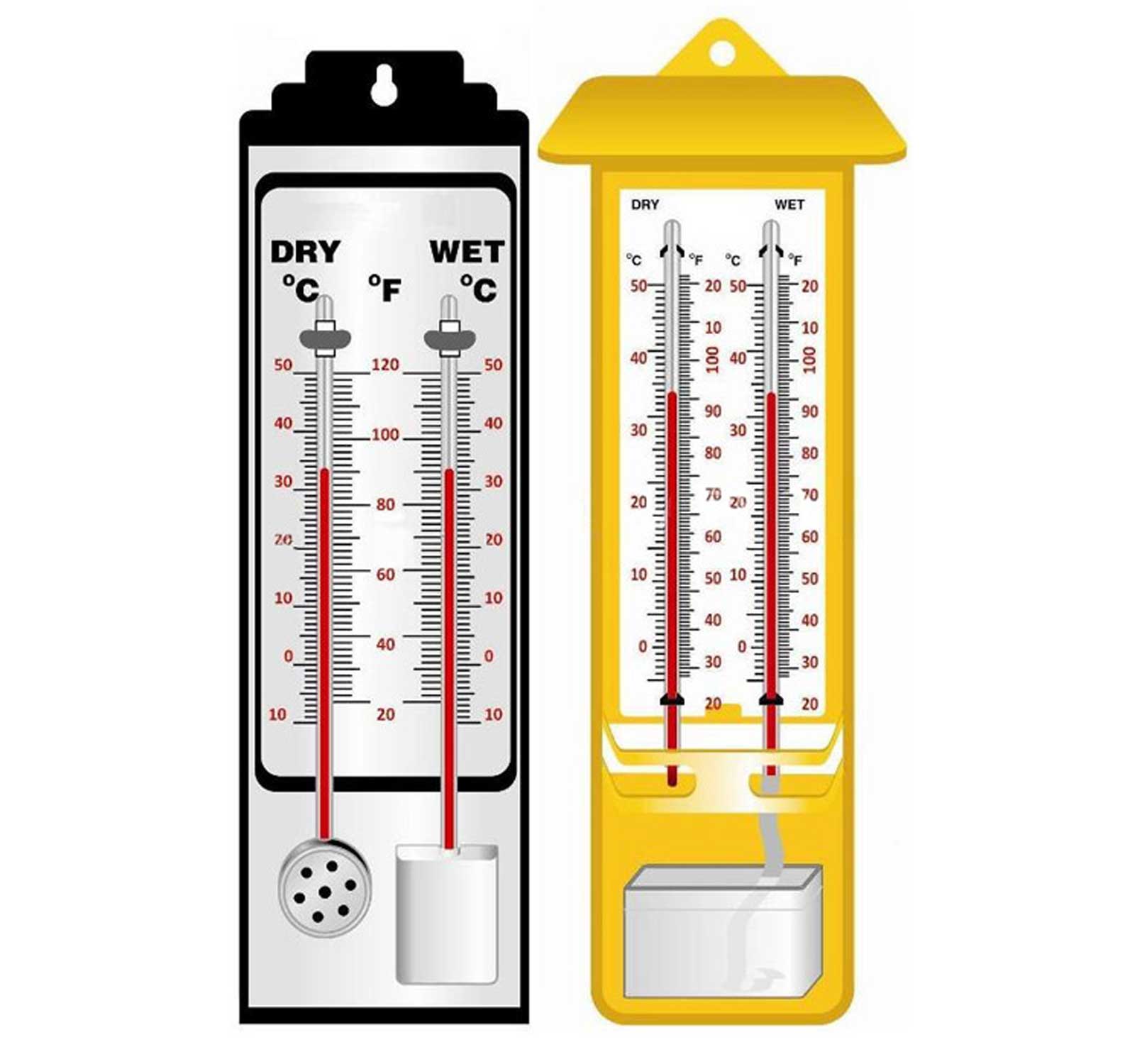
Wet and dry bulb thermometer diagram
The wet bulb temperature is crucial for the design and dimensioning of a cooling tower. A cooling tower cools water by evaporation to temperatures that are lower than the ambient temperature and that approach the wet bulb temperature.
Air start conditions Altitude m. Dry Bulb Temp. Wet Bulb Temp. Dew point Rel. Humidity Abs. Humidity Enthalpy. Wet Bulb Temp Dew point Rel.
Wet and dry bulb thermometer diagram
A hygrometer is a useful gadget that measures relative humidity. This aids in the measurement of water vapour. This device is excellent for detecting water vapour in soil, air, or any other confined place. This is a particularly helpful tool for monitoring humidity. A hygrometer is used to measure the amount of water vapour in the air, soil, and enclosed places. Instruments for measuring humidity typically rely on measurements of other values, such as temperature , pressure , mass, or a mechanical or electrical change in a substance caused by the absorption of moisture. By calibrating and calculating these measured quantities, humidity can be determined. In , Leonardo da Vinci developed a primitive hygrometer. In , Swiss polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert devised a version that was more contemporary. There are two bulbs in a hygrometer: one moist and one dry. One of the bulbs is covered with a wet or dry towel to simulate a thermometer. After a length of time, the water on the bulb evaporates, and the temperature of each bulb is then measured.
Some practice with examples will help. Related to wet-and-dry-bulb thermometer: maximum and minimum thermometer.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser. A psychrometric chart presents physical and thermal properties of moist air in a graphical form. It can be very helpful in troubleshooting and finding solutions to greenhouse or livestock building environmental problems. Understanding psychrometric charts can help you visualize environmental control concepts, such as why heated air can hold more moisture or, conversely, how allowing moist air to cool will result in condensation. This article explains how characteristics of moist air are used in a psychrometric chart. Three examples are used to illustrate typical chart use and interpretation.
Date: circa Inventory Number: DW Classification: Thermometer. Maker: J. Connelot ca. Europe ,. Paris ,. Dimensions: 5. The instrument consists of two thermometers that are each about a foot long, but on a 17 inch enameled frame. One of the thermometers is exposed directly to the air, whereas the other, otherwise identical, is wrapped in a cloth that is affixed to a vertical glass tube on the side of the frame.
Wet and dry bulb thermometer diagram
Although the principles of psychrometry apply to any physical system consisting of gas-vapor mixtures, the most common system of interest is the mixture of water vapor and air, because of its application in heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning and meteorology. In human terms, our thermal comfort is in large part a consequence of not just the temperature of the surrounding air, but because we cool ourselves via perspiration the extent to which that air is saturated with water vapor. Many substances are hygroscopic , meaning they attract water, usually in proportion to the relative humidity or above a critical relative humidity. Such substances include cotton, paper, cellulose, other wood products, sugar, calcium oxide burned lime and many chemicals and fertilizers. Industries that use these materials are concerned with relative humidity control in production and storage of such materials. Relative humidity is often controlled in manufacturing areas where flammable materials are handled, to avoid fires caused by the static electricity discharges that can occur in very dry air. In industrial drying applications, such as drying paper, manufacturers usually try to achieve an optimum between low relative humidity, which increases the drying rate, and energy usage, which decreases as exhaust relative humidity increases.
3 bedroom houses for sale in northampton
Important Links. At air temperatures above zero, the aspiration psychrometer is the most reliable instrument for measuring air humidity and temperature. Commercial and domestic saunas use both a thermometer and a hygrometer to measure the air quality. Evaporation is often used in hot weather to cool ventilation air. Wet Bulb temperature can be measured by using a thermometer with the bulb wrapped in wet muslin. A barometer is used to measure the surrounding air's atmospheric pressure, while a hygrometer measures atmospheric humidity. For example, to decrease relative humidity in a winter greenhouse during a critical time period, we could heat the air. In , Swiss polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert devised a version that was more contemporary. Because it is not affected by the temperature, the volume of the air is also inrelevant. This equipment typically relies on measurements of variables such as temperature, pressure, and weight, as well as a fundamental mechanical or electrical change as moisture is concentrated. A hygrometer is a useful gadget that measures relative humidity.
Last updated: March 6, I f you've ever been in the dry of a desert or the sopping steamy heat of a rainforest, you'll certainly remember it. What makes these extreme environments so different from one another is their humidity : the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere.
Encyclopedia browser? The relationship between the evaporation from the wet bulb and the relative humidity is inverse. Some practice with examples will help. In the weather-station. Altitude: Standard the altitude is set to sea level. Dry-bulb temperature - T db , can be measured using a normal thermometer freely exposed to the air but shielded from radiation and moisture. The free end of this muslin sleeve dips in the reservoir or container filled with distilled water. Modify the access date according your visit. The Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition If you want to promote your products or services in the Engineering ToolBox - please use Google Adwords. Subscribe to: Post Comments Atom. The Dew Point is the temperature where water vapor starts to condense out of the air the temperature at which air becomes completely saturated. When air is cooled, the relative humidity increases until saturation is reached and condensation occurs.

Has understood not all.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.
Interestingly, and the analogue is?