What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
In the process of photosynthesis, plants and other photosynthetic producers create glucose, which stores energy in its chemical bonds. Then, both plants and consumers, such as animals, undergo a series of metabolic pathways—collectively called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration extracts the energy from the bonds in glucose and converts it into a form that all living things can use. Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose. While the process can seem complex, this page takes you through the key elements of each part of cellular respiration.
What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration
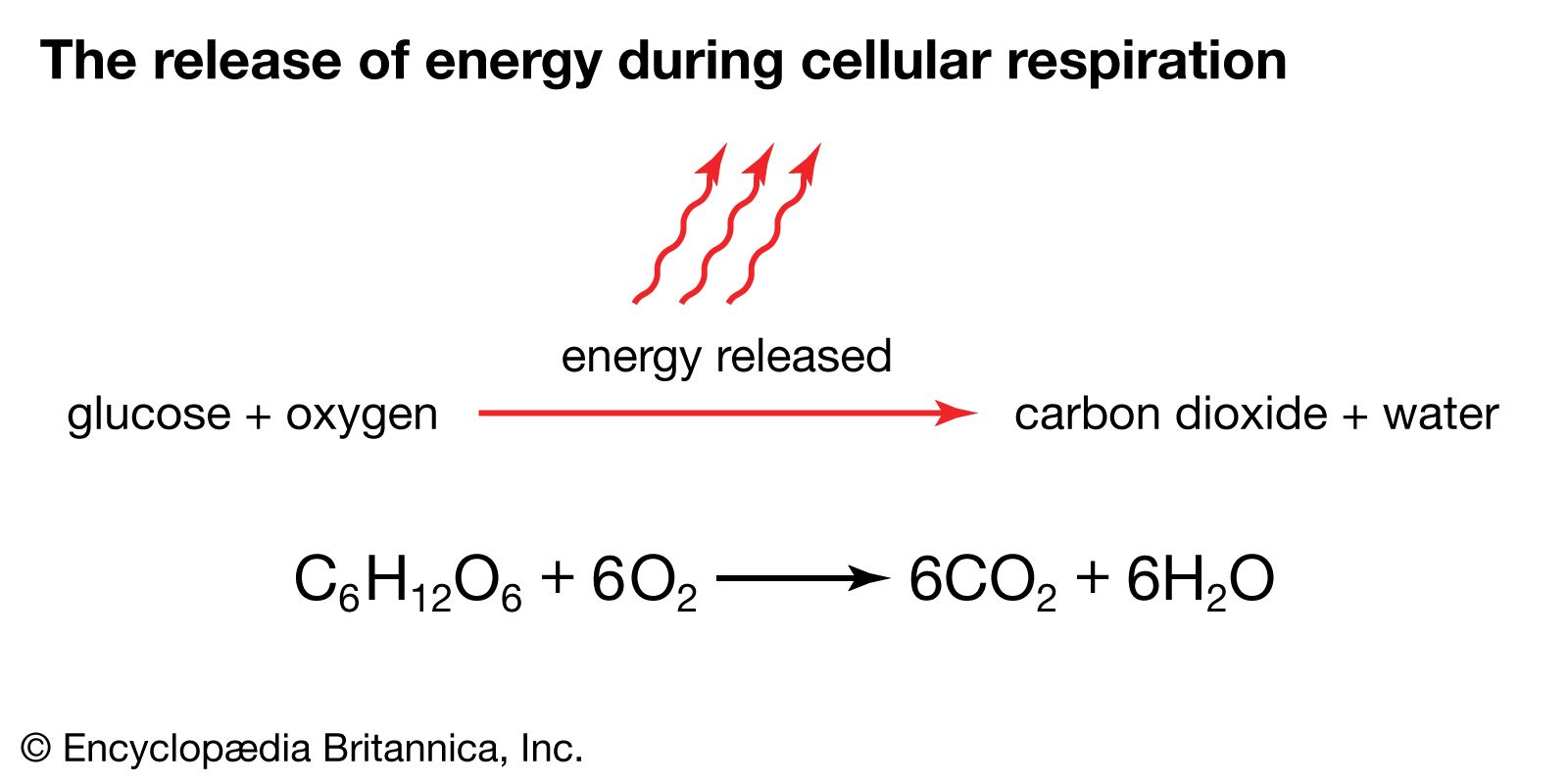
Glucose and oxygen are the reactants and the end products are carbon dioxide and water with the liberation of energy in form of ATP. Cellular respiration occurs in living cells. It provides energy to the cell for carrying out its metabolic activities. Glucose C6H12O6 is the substrate. Cellular respiration occurs in 2 steps: Glycolysis and Kreb's cycle or Citric acid cycle. Glucolysis occurs in absence of oxygen. Glucose is converted into fructose 1;6 di-phosphate that is converted into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid in a series of steps of glycolysis. Pyruvic acid is converted into oxalacetate that enters Kreb's cycle. Kreb's cycle occurs in presence of oxygen. This process is termed oxidative phosphorylation. What are the reactants and end products of cellular respiration? Krishan T.
Step 6. Cellular respiration occurs in 2 steps: Glycolysis and Kreb's cycle or Citric acid cycle. Step 3.
.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cellular respiration. Key Terms. Term Meaning Cellular respiration The process by which organisms break down glucose into a form that the cell can use as energy ATP Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in living things Mitochondria The eukaryotic cell structure where cellular respiration occurs Cytoplasm The contents of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope; includes cytosol which is the jelly-like substance that fills the space between organelles Aerobic Process that requires oxygen Anaerobic Process that does not require oxygen Fermentation An anaerobic pathway for breaking down glucose.
What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration
While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. It moves your internal organs around. It enhances respiration. It is an igniter of great expectations. Glucose, or sugar, has the chemical formula C6H12O6.
Oriental markets near me
This complex protein acts as a tiny generator, turned by the force of the hydrogen ions diffusing through it, down their electrochemical gradient. The third complex is composed of cytochrome b, another Fe-S protein, Rieske center 2Fe-2S center , and cytochrome c proteins; this complex is also called cytochrome oxidoreductase. Where does the water go after being produced as a byproduct? Skip to main content. A carbonyl group on the 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is oxidized to a carboxyl group, and 3-phosphoglycerate is formed. Cellular respiration is where glucose is broken down into its chemical potential energy and stored as ATP Adenosine triphosphate. This is an example of substrate-level phosphorylation. These atoms were originally part of a glucose molecule. Key Terms. Want to join the conversation?
.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Oxygen continuously diffuses into plants; in animals, it enters the body through the respiratory system. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic. The cells get more energy, but at the cost of using more resources. Enolase catalyzes the ninth step. But it is also produced during ETC so basically the net water is product. The overall equation for aerobic cellular respiration is:. Pyruvate oxidation can only happen if oxygen is available. Glycolysis begins with the six carbon ring-shaped structure of a single glucose molecule and ends with two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate Figure 1. Glycolysis consists of two parts: The first part prepares the six-carbon ring of glucose for cleavage into two three-carbon sugars. There, pyruvate will be transformed into an acetyl group that will be picked up and activated by a carrier compound called coenzyme A CoA. Therefore, a concentration gradient forms in which hydrogen ions diffuse out of the matrix space by passing through ATP synthase. How is glycolysis related to the citric acid cycle? The first step in glycolysis is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. The heme molecules in the cytochromes have slightly different characteristics due to the effects of the different proteins binding them, giving slightly different characteristics to each complex.

0 thoughts on “What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration”