What happened during benjamin harrisons presidency
After moving to Indianapolishe established himself as a prominent local attorney, Presbyterian church leader, and politician in Indiana.
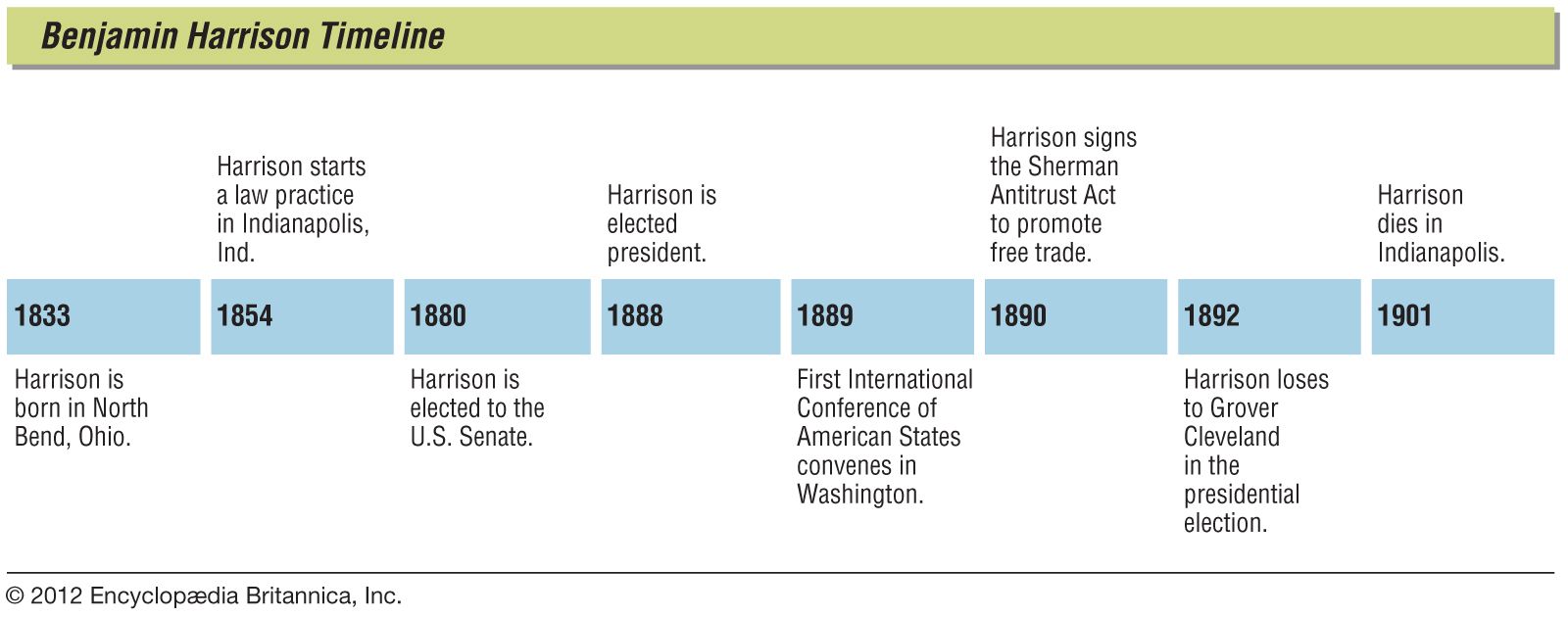
Benjamin Harrison 's term as the president of the United States lasted from March 4, , until March 4, Harrison, a Republican , took office as the 23rd United States president after defeating Democratic incumbent President Grover Cleveland in the election. Four years later he was defeated for re-election by Cleveland in the presidential election. Harrison and the Republican-controlled 51st United States Congress derided by Democrats as the "Billion Dollar Congress" enacted the most ambitious domestic agenda of the late-nineteenth century. Hallmarks of his administration include the McKinley Tariff , which imposed historic protective trade rates, and the Sherman Antitrust Act , which empowered the federal government to investigate and prosecute trusts. Due in large part to surplus revenues from the tariffs, federal spending reached one billion dollars for the first time during his term.
What happened during benjamin harrisons presidency
Coffee-table history books depict Benjamin Harrison as a lightweight puppet of political party bosses. He is often viewed as little more than a "human iceberg" who sleepwalked through the presidency. We are told that while he could sway a crowd of 30, with powerful speeches, he could not talk for two minutes in a room of five people. Because of his lack of personal passion and the failure of anything truly eventful, such as a major war, during his administration, Harrison, along with every other President from the post-Reconstruction era to , has been assigned to the rankings of mediocrity. He has been remembered as an average President, not among the best but certainly not among the worst. Since the s, however, historians have given Harrison higher marks. In foreign affairs, Harrison is now credited with having done more to move the nation along the path to world empire than any previous President, serving as a model for the young Theodore Roosevelt to admire and emulate. His commercial reciprocity treaties, support for the annexation of Hawaii, establishment of the first American protectorate in Samoa, and push for a trans-isthmus canal in Central America set the agenda for the next thirty years of American foreign policy. Where he is found lacking by historians has less to do with his personality and style than with his blindness to a domestic reality that simply overwhelmed him, along with every other political leader of the times: His misguided support for the McKinley Tariff and Sherman Silver Purchase Act may have contributed greatly to the economic collapse of —the greatest depression in American history up to that time. He seemed insensitive and unaware of the massive industrial changes that had overtaken America; of the poverty that Jacob Riis wrote about in his classic study How the Other Half Lives published in ; of the depths of economic hardship affecting the nation's farmers as they fell down the economic ladder to tenancy; and of the industrial crisis that began to topple railroads, banks, and business corporations like dominoes within days of his retirement from office. On the other hand, in those areas which mattered to him—the conservation of national resources, the linkage of world markets to national prosperity, and the civil rights of African Americans—few post-Reconstruction Presidents stood on firmer ground or tried to accomplish more. When compared with the Roosevelts, Wilson, and Truman—activist Presidents of the twentieth century, men who fought wars, managed empires, and confronted economic depressions—Harrison's ranking looks average.
Six days later, 8, militiamen accompany and protect the Pinkerton men. Bush — G.
Not only was he the 23rd president serving from , but he was also the centennial president, inaugurated years after George Washington. Harrison put national strength first, yet arbitration and noninterference would be the policy. He proclaimed:. Harrison was truly one of the first American presidents to succeed in foreign policy and matters beyond our shores. He increased the nation as a player in global trading and therefore dealt with the resulting tariff issues.
Benjamin Harrison 's term as the president of the United States lasted from March 4, , until March 4, Harrison, a Republican , took office as the 23rd United States president after defeating Democratic incumbent President Grover Cleveland in the election. Four years later he was defeated for re-election by Cleveland in the presidential election. Harrison and the Republican-controlled 51st United States Congress derided by Democrats as the "Billion Dollar Congress" enacted the most ambitious domestic agenda of the late-nineteenth century. Hallmarks of his administration include the McKinley Tariff , which imposed historic protective trade rates, and the Sherman Antitrust Act , which empowered the federal government to investigate and prosecute trusts. Due in large part to surplus revenues from the tariffs, federal spending reached one billion dollars for the first time during his term. Harrison facilitated the creation of the National Forests through an amendment to the General Revision Act , and substantially strengthened and modernized the United States Navy.
What happened during benjamin harrisons presidency
After moving to Indianapolis , he established himself as a prominent local attorney, Presbyterian church leader, and politician in Indiana. Senate as a brevet brigadier general of volunteers in Harrison unsuccessfully ran for governor of Indiana in The Indiana General Assembly elected Harrison to a six-year term in the Senate, where he served from to
Ticketmaster mexico
During the construction Congress created the Bureau of Immigration under the Department of the Treasury. Harrison states that all members of his cabinet are in favor of war with Chile. It was clear that Harrison would not be re-nominated unanimously. Many lending institutions and corporate powers balked, and the value of the U. New Georgia Encyclopedia. Harrison died from pneumonia at his home in Indianapolis on March 13, , at the age of In Rigsby, Enrique D. Populist Party candidate James B. The matter was sent to an international court of arbitration in Paris. Blaine , the party's nominee in the presidential election. Harrison and the president were vigorously criticized. When the Great Railroad Strike of reached Indianapolis, he gathered a citizen militia to make a show of support for owners and management, [25] [69] and helped to mediate an agreement between the workers and management and to prevent the strike from widening.
In , Harrison signed into law the Sherman Antitrust Act, the first piece of legislation designed to prohibit industrial combinations, or trusts. Before the end of his first term, support for Harrison was waning even within the Republican Party.
Harrison's wife Caroline began a critical struggle with tuberculosis earlier in , and two weeks before the election, on October 25, she died from the disease. Many believed the cottage gift appeared improper and amounted to a bribe for a cabinet position. Retrieved March 17, Postage stamps , more than most other U. In foreign affairs, Harrison reaffirmed the Monroe Doctrine as a mainstay of foreign policy, while urging modernization of the Navy and a merchant marine force. Harrison, Mary Lord ed. When is he in fact to have those full civil rights which have so long been his in law? Rhodes, James Ford. Many citizens firmly believed they were guilty, and that the jury had been corrupted. In office March 4, — March 4, Eisenhower John F. Download as PDF Printable version. Harrison and Blaine hoped to reach agreements at the conference to create a customs union for free trade and establish a system for arbitration of international disputes. Please leave blank.

I join. All above told the truth. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is and it is excellent idea. I support you.