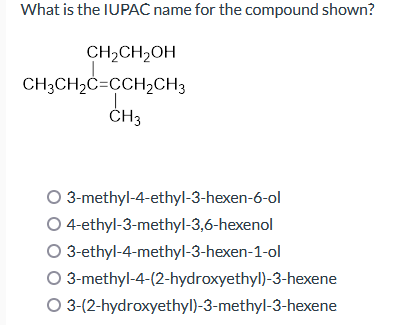
What is the iupac name for the compound shown
In order to give compounds a name, certain rules must be followed. This is to give consistency to the names. It also enables every compound to have a unique name, which is not possible with the common names used for example in industry. We will first look at some of the steps that need to be followed when naming a compound, and then try to apply these rules to some specific examples.
In order to name organic compounds you must first memorize a few basic names. These names are listed within the discussion of naming alkanes. In general, the base part of the name reflects the number of carbons in what you have assigned to be the parent chain. The suffix of the name reflects the type s of functional group s present on or within the parent chain. Other groups which are attached to the parent chain are called substituents. Alkanes - saturated hydrocarbons The names of the straight chain saturated hydrocarbons for up to a 12 carbon chain are shown below.
What is the iupac name for the compound shown
.
This will determine the suffix of the name see Table 4. The molecule is 4-methylheptan-3,3-diol. Find the longest carbon chain and number the carbons in the longest chain There are six carbons in the longest chain if they are numbered as shown in red on the left.
.
We will only use those common names listed under Objective 3, above. We will use systematic names in all other cases. For example, the systematic name of the compound shown below is benzenecarbaldehyde, but it has the common name of benzaldehyde. The most potent and varied odors are aldehydes. Ketones are widely used as industrial solvents. Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group. Aldehydes are considered the most important functional group. They are often called the formyl or methanoyl group. Aldehydes derive their name from the dehyd ration of al cohols.
What is the iupac name for the compound shown
With the ability to identify functional groups, next we will learn how to give IUPAC names to compounds containing a few functional groups, by following a set of rules. For naming purposes, the functional groups are assigned with priorities Table 2. The order of the groups listed in Table 2. The groups in the subordinate table have no difference in terms of priority, and they are usually listed in the alphabetic order. The carboxylic acid group is always on the 1 position, so it is NOT necessary to include that number for the position. With the multiple groups involved, the ketone has the highest priority, so it decides the last name. The numbers on the chain should start from the left side to ensure that ketone has the lowest number. The naming of the substituent with the benzene ring is bit challenging. In ester, an OR group replaces the OH group of a carboxylic acid. For substituted benzene, the benzene ring is regarded as the parent structure, and the positions and names of substituents are added to the front.
August weather
A6 butanone , C3 4. Draw the structural and condensed structural representations for the organic compound ethyl hexanoate. There are five carbons in the longest chain, so the prefix is pent-. Number the carbons of the parent chain from the end that gives the substituents the lowest numbers. Combine the elements of the name into a single word in the following order: halogen atoms; prefix; name ending according to functional group The name of the compound is 2-chloropropane. This molecule is 1-fluoro-2,2-diiodobutane. The suffix -ene tells us there is a double bond between these carbon atoms. There is a hydroxyl group, therefore the compound is an alcohol and the suffix is -ol. Give the structural formula for each of the following compounds:. The position of the hydroxyl group s on the parent chain is are indicated by placing the number s corresponding to the location s on the parent chain directly in front of the base name same as alkenes. What similarities are there? The parent chain is numbered so that the multiple bonds have the lowest numbers double and triple bonds have priority over alkyl and halo substituents. A3 2-chloroethane , B7 haloalkane.
IUPAC nomenclature is used for the naming of chemical compounds, based on their chemical composition and their structure. Another entity called the International Association of Chemical Societies IACS existed, and on , gave vital propositions the new one should address: [2]. In , a group of chemists created the IUPAC with this idea, as well as the purpose of unionizing scientists and strengthening the international trade of science.
There are only single carbon-carbon bonds, therefore the prefix becomes pentan-. We will only be dealing with the haloalkanes i. Match the compounds in column A with the correct number of carbon atoms in column C. Draw the semi-structural structural and condensed structural formula for the organic compound 2,2,4-trimethylhexane. In this case that is from right to left. Two on carbon 2 and one on carbon 4. The second double bond occurs between carbons 3 and 4. Combine the elements of the compound's name into a single word in the order of branched groups; prefix, name ending according to the functional group The compound's name is butanone or 2-butanone. A5 3-heptyne , B2 alkyne. Draw the structural representation: There are only single carbon-carbon bonds in this compound and no other functional groups, therefore it is an alkane and the suffix is -ane. There is one branched group which is a methyl group and this is at position 2. The hydroxyl group is attached to the second carbon atom. Remember that the main carbon chain must contain both the double bonds. This group has only one carbon atom and is therefore a methyl group 4-methyl.

Bravo, what necessary phrase..., a remarkable idea
I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
It is a valuable phrase