What is the reciprocal ratio of sine
The reciprocal of sine is the cosecant function. There are six main trigonometric functions namely, sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant. An important thing to note is that the reciprocal of sine is not the inverse function of sine, that is, the cosecant function is not the inverse function of sine.
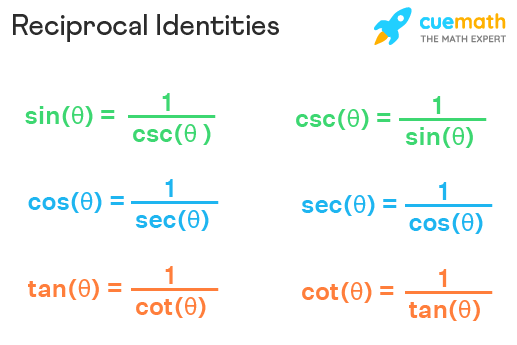
The six trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant, out of which the three standard trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent. The six trigonometric ratios can be grouped in pairs as reciprocals. The reciprocal identities are the reciprocals of these six trigonometric ratios. Note that reciprocal identities are not the same as inverse trigonometric functions. Reciprocal identities are the reciprocals of the six fundamental trigonometric functions sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent. It is obtained by interchanging the values of numerator and denominator. Similarly, we can find the reciprocal of each trigonometric ratio using their definitions.
What is the reciprocal ratio of sine
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. The reciprocal trigonometric ratios. About About this video Transcript. Sal finds all six trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent of an angle in a given right triangle. Created by Sal Khan. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted.
Share your thoughts in the comments.
Trigonometry is all about triangles or to be more precise about the relation between the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. In this article, we will be discussing about the ratio of sides of a right-angled triangle with respect to its acute angle called trigonometric ratios of the angle and find the reciprocals of these Trigonometric Ratios. The trigonometric ratios of an acute angle in a right triangle are the relationship between the angle and the length of two sides. The ratios defined below are abbreviated as sin C, cos C, and tan C respectively. Reciprocals of basic trigonometric ratios are the inverse values of the sin, cos, and tan values that are computed by reciprocating the sides required for computing the ratio. You will see that cosec A, sec A, and cot A are respectively, the reciprocals of sin A, cos A, and tan A from the following diagrams and examples. Sine is the ratio of the opposite side to the Hypotenuse.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. The reciprocal trigonometric ratios. About About this video Transcript. Sal finds all six trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent of an angle in a given right triangle.
What is the reciprocal ratio of sine
Suppose you want to build a ramp for access to a loading dock that is 4 feet above ground level. How long does the ramp have to be? In this diagram, you have a right triangle for which you know the length of one side and the measure of an acute angle. You want to find the length of the hypotenuse. You may know that the Pythagorean Theorem enables you to find the length of one side of a right triangle, given the lengths of the other two sides. Now you will learn trigonometry, which is a branch of mathematics that studies the relationship between angles and the sides of triangles. In fact, trigonometry will allow you to find unknown side lengths and angle measures in right triangles in a variety of cases, such as in the problem above. In trigonometry, this type of relationship between sides and angles is very important.
Millie bobby brown cumtribute
That's how my mind works, anyway. The formula of reciprocal of sine is:. Improved By :. Last Updated : 29 Feb, Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free. The hypotenuse would be the same regardless of what angle you pick, but the opposite and the adjacent is dependent on the angle that we choose in the right triangle. And what's the hypotenuse? The hypotenuse is right over here, it's opposite the 90 degree angle. We know that the derivative of sin x is cos x. It tells us that the tangent of an angle is equal to the opposite side over the adjacent side. And then we can get the other three by looking at the first three. Reciprocal of Sine Problems. Flag Button navigates to signup page.
The reciprocal of sine is the cosecant function. There are six main trigonometric functions namely, sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant. An important thing to note is that the reciprocal of sine is not the inverse function of sine, that is, the cosecant function is not the inverse function of sine.
So what is the cotangent of A? Vishal Mishra. Reciprocals of basic trigonometric ratios are the inverse values of the sin, cos, and tan values that are computed by reciprocating the sides required for computing the ratio. Then switch the numerator and denominator. Graph of Reciprocal of Sine 5. So, we have cosecant which is the reciprocal of sine. Improved By :. Share your suggestions to enhance the article. What Are Trigonometric Reciprocal Identities? It's length 5. Our Mission. Direct link to a. Engineers, architects, astronomers, geologists, navigators, and scientists use them every day. The reciprocal of the sine function is a trigonometric function , called the cosecant function. Trig is used in many t

0 thoughts on “What is the reciprocal ratio of sine”