What muscles do the plank work
Ah, planks. But anyone who's ever taken a group fitness class knows that they are a deceptively difficult exercise. A plank is an isometric exercise that involves getting into a push-up position, and then staying put, explains physical therapist Grayson WickhamD. Yes, this equipment-free move works your core, upper body, and lower body.
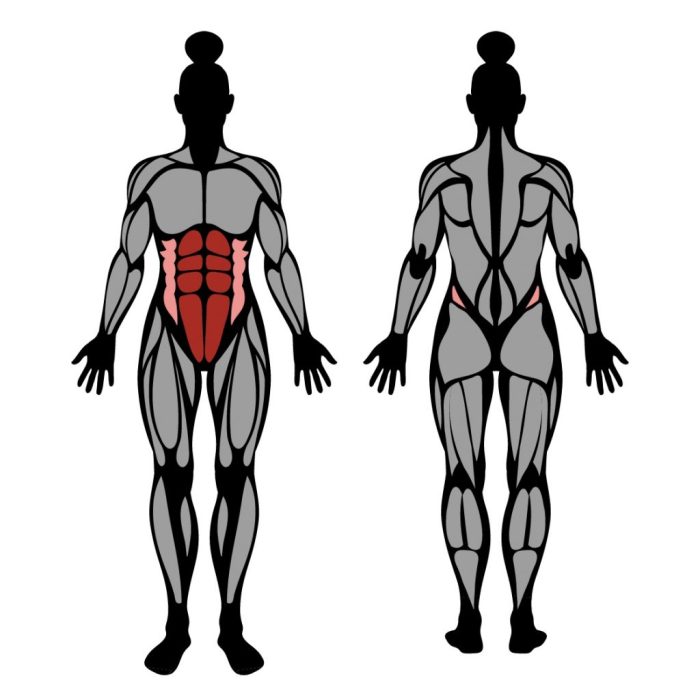
We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Why Trust Us? Planks are the ultimate test of total-body strength, not just your core. This targets a wide range of muscles, especially the rectus and transverse abdominis, Blades says. The rectus abdominis are the front muscles in the abdomen that support the muscles of the spine and help keep organs in the abdomen area in place. In fact, a weak TVA is often the culprit of lower back pain. You can further engage your shoulders and back muscles in a plank when you grip the floor more with your fingers and hands.
What muscles do the plank work
Exhibit one: the plank. In its most basic form, the plank is exceedingly straightforward—just assume a pushup position with your arms straight or forearms on the floor and hold that posture for the prescribed amount of time or for as long as you can before failure. But despite its simplicity, the plank can help you build core strength more quickly than most other abdominal exercises—especially those that involve movement, like the crunch—according to a study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. There are no reps, no top or bottom of the movement, none of the fleeting relief that comes from transitioning from contraction to elongation, and vice versa. There is only constant contraction on a head-to-toe scale that must be held until you can hold it no more. As a result, few other exercises can compare to the plank when it comes to muscular activation and time under tension the undisputed king of muscle-building stimuli. But like every other exercise, you need to execute the plank with proper form to maximize its benefits and ensure that you target the right muscles in the most effective way possible. In order to prevent your hips from sagging—a key point of proper form—you must engage another core muscle group that most people associate with the lower body: your glutes. Similarly, the muscles in your neck, shoulders, arms, upper back, and legs will be called into action to keep your posture rigid and your body straight from head to heels. The moment any of them fail and your form falters, the clock stops and the set is over.
Be sure to keep your core arvest.com the entire time. The rectus abdominis are the front muscles in the abdomen that support the muscles of the spine and help keep organs in the abdomen area in place.
Planks can help work your core muscles, as well as your upper and lower body. There are different types of planks that may have slightly different benefits. The plank is a full body exercise, meaning it targets muscles of the upper body, core, and lower body. In particular, your rectus abdominis , obliques, and transverse abdominis are utilized 1 , 2 , 3. The rectus abdominis is the top layer of muscles of your stomach. It helps cinch your waist and stabilize your back muscles 4 , 5. Furthermore, your inner and outer obliques and spinal erectors back muscles are engaged during the plank.
Planks can help work your core muscles, as well as your upper and lower body. There are different types of planks that may have slightly different benefits. The plank is a full body exercise, meaning it targets muscles of the upper body, core, and lower body. In particular, your rectus abdominis , obliques, and transverse abdominis are utilized 1 , 2 , 3. The rectus abdominis is the top layer of muscles of your stomach. It helps cinch your waist and stabilize your back muscles 4 , 5. Furthermore, your inner and outer obliques and spinal erectors back muscles are engaged during the plank. When the obliques on both sides of your body work in tandem, they also provide a stabilizing effect, particularly by holding the ribs and hips in alignment 1 , 2 , 3. The muscles of your upper body, such as the trapezius , rhomboid major and minor, latissimus dorsi, pectorals chest muscles , serratus anterior , deltoids, biceps, and triceps, also work hard during a plank 2.
What muscles do the plank work
There are many benefits of planking as planks are an excellent abdominal and core exercise. To ensure you keep your core strong and stable, add the plank to your ab workout program. Keep reading to find out plank exercise benefits, and different types of plank exercises along with instructions. Planking provides many physical benefits. Strengthening the core is an important aspect of any workout regimen. A strong and solid core looks and feels good. But more importantly, it helps to stabilize, balance, and power the body during just about every other activity.
Tamarind modern indian bistro
The rectus abdominis is the top layer of muscles of your stomach. We're testing the Lululemon product for you and weighing in on whether the trend has past or if it's still worth the hype. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Try to hold the position for a minimum of 10 seconds or longer. The plank is a full body exercise, meaning it targets muscles of the upper body, core, and lower body. Plank jacks are a combined cardiovascular and strength-building exercise that can help you boost core and upper body strength. Share this article. The body is good at compensating for weaknesses by forcing other, stronger muscles to take over the work for weaker muscles, he says. Start on all fours on the ground. What muscles do a side plank work? If you just move your arms or leg on their own, it works these muscles less, if you move your arms and legs at the same time, the deadbug works these muscles much more. For a modified plank, Blades suggests dropping to your knees instead of holding yourself up on your toes. Day 1 is focuses on doing more total planking time, whilst day 2 focuses on building the plank itself. Search Search. How often should I plank?
Planks are a great way to build up your core strength. But in addition to your abs, planks activate many other muscles throughout the body.
The two main variations of the plank exercise include the forearm plank and the straight-arm plank. Adjust so wrists are stacked under shoulders, and knees are bent and under hips. So, when your hip and side glutes are weak, your lower back usually takes over the work which can result in overuse injuries, as well as generalized aches and pains. For those folks, the below plank variations may be better. If you just move your arms or leg on their own, it works these muscles less, if you move your arms and legs at the same time, the deadbug works these muscles much more. Muscles used Benefits How to do it Common mistakes Variations Bottom line Planks can help work your core muscles, as well as your upper and lower body. Your abdominal muscles support your lumbar spine lower back , helping provide structural stability and assist with pelvis movement. Ah, planks. Fitness Tips. How to Incorporate. The plank is a great exercise for increasing core strength, reducing the risk of back injury, and improving athletic performance. You can further engage your shoulders and back muscles in a plank when you grip the floor more with your fingers and hands. Learn about your different heart rate zones…. Good news: There really is no wrong way to incorporate planks into your exercise routine. Squeeze glutes and quads to maintain a straight line from head to heels.

I think, that you commit an error. Let's discuss.