When calcium carbonate is heated
Byju's Answer. When calcium carbonate is heated, it gives calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. Is this reaction reversible or irreversible? Open in App.
In association with Nuffield Foundation. Calcium carbonate is strongly heated until it undergoes thermal decomposition to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. This experiment can be carried out conveniently in groups of two or three and takes about 40—45 minutes. Keep an eye on less mature students who might be tempted to suck rather than blow through the filtrate. This set of experiments involves a variety of important reactions and types of reactions, with several references to industrial processes. The roasting of limestone and the hydration of the quicklime formed has relevance in the manufacture of plaster and cement, and in the laboratory limewater is a common reagent for the testing of carbon dioxide. Students could be asked to carry out web research on these applications.
When calcium carbonate is heated
.
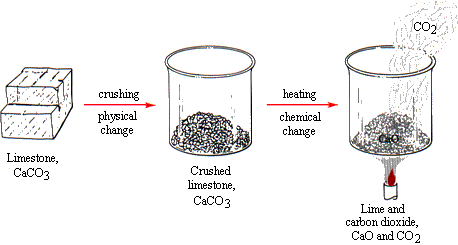
Physical and Chemical Changes. Use Practical experiments.
.
Calcium carbonate, calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide are all made from limestone and have important applications so it is important to know how they are made. Calcium carbonate is found naturally in limestone close limestone A type of sedimentary rock. When limestone is heated strongly, the calcium carbonate it contains absorbs heat endothermic close endothermic Reaction in which energy is taken in. This is indicated by an orange glow as the limestone is heated. Calcium oxide also known as quicklime is a key ingredient in the making of cement and is also used to make certain types of plaster. Calcium oxide reacts with a few drops of water to form calcium hydroxide, which is an alkali close alkali A base which is soluble in water. This is an exothermic close exothermic Reaction in which energy is given out to the surroundings. The surroundings then have more energy than they started with so the temperature increases. The solid remains white but crumbles into a powder as the water is added. Calcium hydroxide also known as slaked lime is used to neutralise close neutralise To be made neutral by removing any acidic or alkaline nature.
When calcium carbonate is heated
Calcium carbonate is the principal mineral component of limestone. Its chemical and physical properties lie behind the modern-day uses of limestone as well as the unique limestone landscapes of the countryside. The principal mineral component of limestone is a crystalline form of calcium carbonate known as calcite. Although calcite crystals belong to the trigonal crystal system, shown below, a wide variety of crystal shapes are found. Single calcite crystals display an optical property called birefringence double refraction. This strong birefringence causes objects viewed through a clear piece of calcite to appear doubled. Another mineral form of calcium carbonate is called aragonite. Its crystal lattice differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape — an orthorhombic system with needle-shaped crystals. Calcium carbonate is unusual in that its solubility increases as the temperature of the water decreases.
Teens see thru
Physical and Chemical Changes. Related articles. No comments yet. You're not signed in. Site powered by Webvision Cloud. By Kirsty Patterson. In association with Nuffield Foundation. Blow bubble through the solution. Freshly purchased drinking straws should be used and each student issued with their own straw. Use this practical to investigate how solutions of the halogens inhibit the growth of bacteria and which is most effective. This practical lets learners distil and tablets and answer that very question. Blackboard chalk should not be used as it is likely to be mostly calcium sulfate.
In association with Nuffield Foundation.
Add 10 cm 3 more water. This experiment can be carried out conveniently in groups of two or three and takes about 40—45 minutes. If grams of carbon dioxide is formed, what is the mass of calcium oxide formed? Experiment Practical potions microscale 11—14 years By Kirsty Patterson Observe chemical changes in this microscale experiment with a spooky twist. This practical lets learners distil and tablets and answer that very question. Additional information This is a resource from the Practical Chemistry project , developed by the Nuffield Foundation and the Royal Society of Chemistry. Students could be asked to carry out web research on these applications. Keep an eye on less mature students who might be tempted to suck rather than blow through the filtrate. The first of three steps, in practical experiments, that show learners how to prepare paracetamol. Heat for 10 minutes. Is this reaction reversible or irreversible? More crumbling, steam given off, evidence that mixture has become hot. Wear eye protection. Add 2—3 drops of water.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.
Bravo, this excellent idea is necessary just by the way