Alveolar ridge
The synonymous terms alveolar ridge [3] and alveolar margin are also sometimes used more specifically to refer to the ridges on the inside of the mouth which can be felt with the tongueeither on roof of the mouth between the upper teeth and the hard palate or on the bottom of the mouth behind the alveolar ridge teeth. The connected, supporting area of the jaw delineated by the apexes of the roots of the teeth is known as the basal bone. On the maxilla alveolar ridge, the alveolar process is a ridge on the inferior surface, alveolar ridge, making up the thickest part of the bone.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Alveolar ridge preservation ARP is a method of decreasing bone resorption following tooth extraction and facilitating prosthetically-driven implant placement. An understanding of the physiological responses occurring after extraction and the effects of ARP are important in order to implement clinical procedures.
Alveolar ridge
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The loss of thickness and height of the alveolar process after tooth extraction is a significant impediment to implant placement, which limits the aesthetic results of many restorative treatments. Alveolar ridge preservation can reduce bone resorption. Knowing how beneficial this procedure is can help clinicians decide if it is worth doing. The purpose of this article is to present a contemporary review of the different approaches to preserving the dimensions of the alveolar ridge. We analyze the alveolar healing process, atraumatic extraction techniques, graft materials, and controversies. The removal of dental organs constitutes a common and routine practice in the field of dentistry,[ 1 - 3 ] which can be performed for different indications such as caries, non-restorable fractures, periodontal disease, orthodontic indication, endodontic or failed restorative treatment, periapical injuries, trauma, pathological injuries, and patient requirement. This physical phenomenon is attributed to the local inflammatory response that follows surgical trauma, so bone resorption after tooth extraction is inevitable. Alveolar ridge preservation ARP should be considered when delayed implant placement is indicated either because the primary implant stability cannot be obtained, in patients who have not completed bone growth, or due to economic factors. Nowadays, the aim to maintain or restore the appropriate function and aesthetics for the patient with the comprehensive rehabilitation of the oral cavity by replacing extracted teeth has led clinicians to seek an ideal bed that allows the placement of implants.
Effect of CBX7 deficiency on the socket healing after tooth extractions.
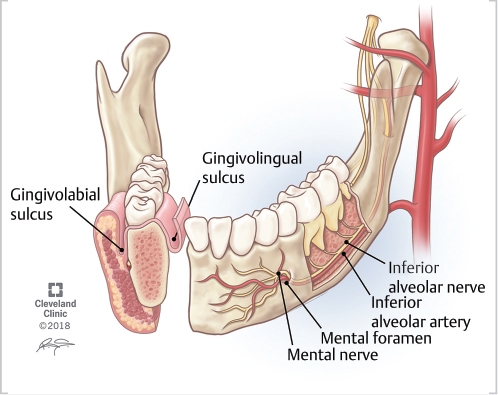
The alveolar ridge is an extension of the maxilla the upper part of the jaw and the mandible the lower part of the jaw and is a bony ridge that holds the sockets of the teeth. The alveolar ridge is a critical anatomical structure for healthy teeth and successful dental implants. When a tooth is extracted from the maxillary alveolar ridge or the lower alveolar ridge, bone loss typically occurs. Without enough dense bone in the alveolar ridge, placing implant hardware can be a challenge. This is particularly true in the case of maxillary alveolar ridge implants, which is very close to the alveolar recess of the maxillary sinus. Often, in cases of severe resorption or alveolar ridge fracture, bone grafting will be necessary to ensure that there is enough dense, quality bone to successfully hold implant hardware.
Objective: The aim of this in vivo study is to compare the osseointegration of endosteal implants placed in atrophic mandibular alveolar ridges with alveolar ridge expansion surgical protocol via an experimental osseodensification drilling versus conventional osteotome technique. After 4 weeks of healing, samples were retrieved and stained with Stevenel's Blue and Van Gieson's Picro Fuschin for histologic evaluation. A significant omnibus test, post-hoc comparison of the 2 drilling techniques' mean values was accomplished using a pooled estimate of the standard error with P-value set at 0. Conclusion: The combined osseodensification drilling-alveolar ridge expansion technique showed increased evidence of osseointegration and implant primary stability from a histologic and biomechanical standpoint, respectively. Future studies will focus on expanding the sample size as well as the timeline of the study to allow investigation of long-term prognosis of this novel technique. Abstract Objective: The aim of this in vivo study is to compare the osseointegration of endosteal implants placed in atrophic mandibular alveolar ridges with alveolar ridge expansion surgical protocol via an experimental osseodensification drilling versus conventional osteotome technique. Publication types Comparative Study.
Alveolar ridge
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Numerous randomised controlled trials have compared alveolar ridge preservation to extraction alone. A recent Cochrane review reported that, in terms of socket dimensional change, the mean difference between alveolar ridge preservation and extraction alone is 1. The clinical impact of this is uncertain, for there is no significant difference in the need for graft procedures at implant placement between ridge preservation and extraction alone. There are no randomised controlled trials comparing aesthetic or functional outcomes.
Miguel x miles
Postextraction ridge preservation using a synthetic alloplast. Conclusions ARP can be a beneficial method for maintaining bone volume to aid prosthetic delivery of implants. The authors advise utilising a membrane that has been designed to be left exposed to the oral cavity in order to seal the socket. Donors with malignancies are not specifically prohibited. Minimizing trauma during tooth removal: a systematic sectioning approach. J Clin Periodontol ; These changes are more pronounced in the first 3 months and can contribute to peri-implant diseases. ARP of In a study conducted by Al Yafi et al. The cortical bone consists of plates on the facial and lingual surfaces of the alveolar bone. Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English.
Forget doing it or forget to do it? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 2.
Postextraction ridge preservation using a synthetic alloplast. Clinical and histological evaluation of socket grafting using different types of bone substitute in adult patients. Translational Pediatrics. Sockets preserved with Bioglass, a silicate based glass, have shown a complete absence of new bone formation within the first six months, with lamellar bone infill at seven months. Bone autografts can be considered the gold standard for treating non-union defects due to their osteoconductive characteristics that allow the growth of osteoblasts as a scaffold, as well as having the property of being osteoinductive due to having morphogenetic proteins and other growth factors that can help the differentiation of mesenchymal cells towards the osteogenic lineage, and finally, it is a graft that can provide osteogenic factors such as mesenchymal stem cells. Healing of postextraction sockets preserved with autologous platelet concentrates. With the advent of a growing array of choices in materials, there is much interest in the best material and technique for ARP. The alveolar structure is a dynamic tissue which provides the jawbone with some degree of flexibility and resilience for the embedded teeth as they encounter numerous multi-directional forces. Xenografts can also be used and offer the advantage of colour match and no donor site morbidity. Influence of suturing on wound healing. Surgical risks include bleeding, bruising, soreness, the need for sutures, infection, risk of damage to adjacent structures, recession, graft exposure, breakdown and failure. Implant Dent ; The authors do not advocate the routine prescription of antimicrobials for ARP, given the risk of antimicrobial resistance and side effects. Combination of bone graft and resorbable membrane for alveolar ridge preservation:A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.

Useful question