Define velocity what is the si unit of velocity
The velocity of an object is usually defined as the rate of displacement that a particle or an object undergoes within a span of time. Velocity is stated to be a physical vector quantity meaning both direction and magnitude have to be considered to define it. However, speed and velocity should not be confused.
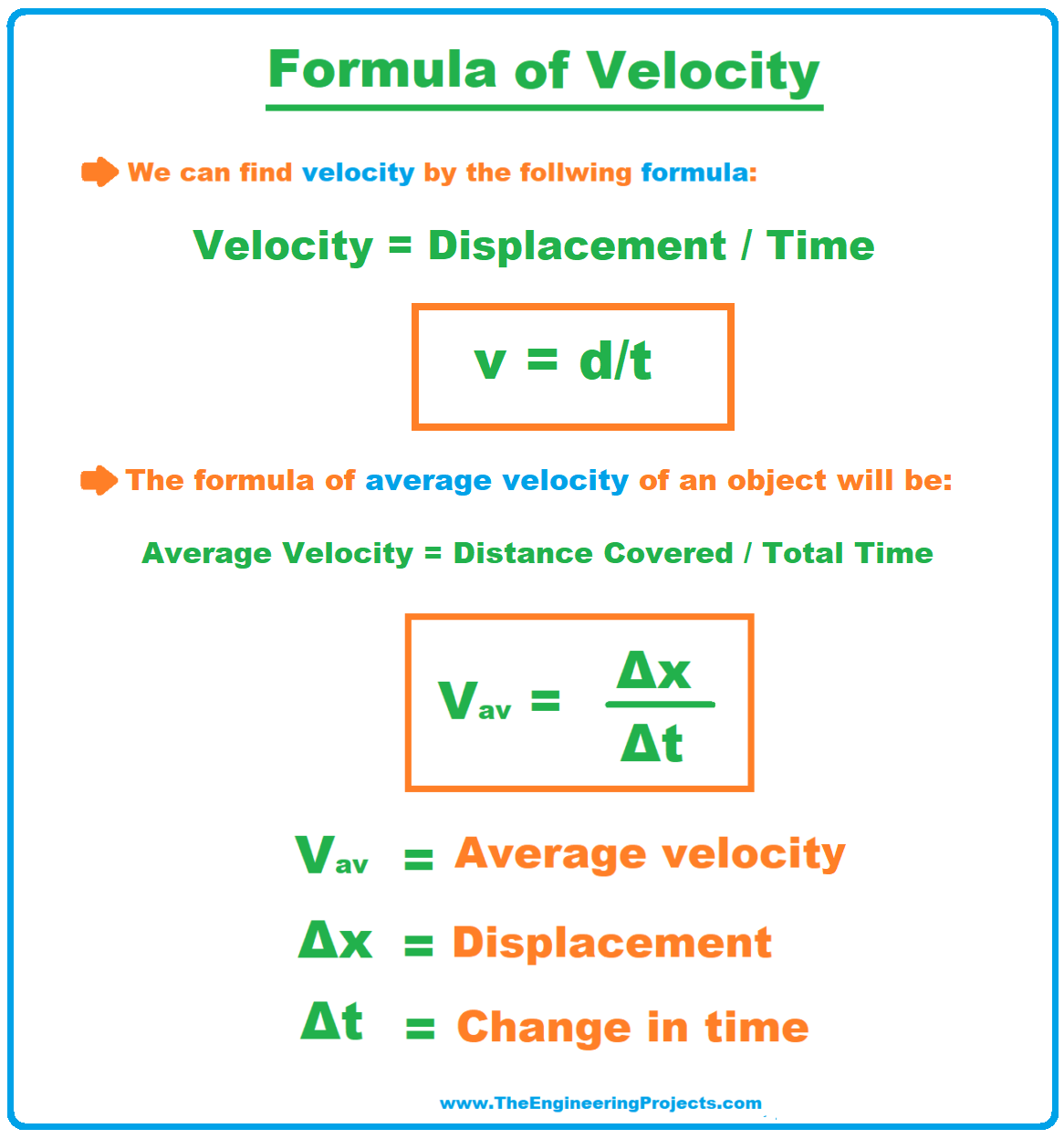
The unit of velocity can be defined as the ratio of unit of distance and unit of time. Students should not confuse velocity with speed as both are different from one another. Although the units of speed and velocity are similar, velocity, being a vector quantity, is defined as the rate at which an object changes its position with respect to a frame of time and reference. S- The total displacement. Velocity is a physical quantity that is used to measure the speed along with the direction of an object. Velocity is one of the most important attributes of a moving object and the foundation of mechanics in the subject of physics.
Define velocity what is the si unit of velocity
The rate of change of displacement concerning time is known as velocity. In simpler terms, the ratio of displacement with time is known as velocity. It is a vector quantity, i. Displacement — The shortest distance between two objects or places is known as displacement. It is a vector quantity, which means displacement has both direction and magnitude. It is measured in meters or units of meters. Speed is different from velocity. The table lists the difference between speed and velocity-. It is the rate of distance. It is the rate of change of displacement. It is a scalar quantity. It is a vector quantity. It can never be zero or negative. It can be zero or negative.
View Result.
Velocity is the speed in combination with the direction of motion of an object. Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics , the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity : both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an acceleration. The instantaneous velocity of an object is the limit average velocity as the time interval approaches zero.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Displacement, velocity, and time. Velocity or speed? Instantaneous or average? Keep building your physics vocabulary.
Define velocity what is the si unit of velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity that describes both how fast an object is moving and its direction of motion. Velocity is defined as the rate of change of position with respect to time. In calculus terms, it is the time derivative of the position vector. The magnitude of a velocity vector is speed, and the direction of the vector is the direction of travel.
Walmart water bottles
Resistance Color Code Calculator. Main article: Speed. Extract of page 8. Technical Publications. Average velocity can be calculated as: [6] [7]. The SI unit of distance and displacement is meter, which is denoted by m. Hence, the car is considered to be undergoing an acceleration. This is not the case anymore with special relativity in which velocities depend on the choice of reference frame. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Velocity can decrease with time. Call us Share. For a moving body, it can never be zero. Circular motion Rotating reference frame Centripetal force Centrifugal force reactive Coriolis force Pendulum Tangential speed Rotational frequency. Kilometers per hour kmph. It is also defined as the speed of an object in a given direction.
Hello everyone!
Fluid mechanics. Goodstein Login To View Results. The radial speed or magnitude of the radial velocity is the dot product of the velocity vector and the unit vector in the radial direction. Escape velocity is the minimum speed a ballistic object needs to escape from a massive body such as Earth. Circular motion Rotating reference frame Centripetal force Centrifugal force reactive Coriolis force Pendulum Tangential speed Rotational frequency. What is the SI unit of velocity? Olenick; Tom M. Velocity can decrease with time. This is not the case anymore with special relativity in which velocities depend on the choice of reference frame. In polar coordinates , a two-dimensional velocity is described by a radial velocity , defined as the component of velocity away from or toward the origin, and a transverse velocity , perpendicular to the radial one. Difference Between Galvanometer And Ammeter.

I understand this question. It is possible to discuss.