Derive lens makers formula
Lenses of different focal lengths are used for various optical instruments. The derivation of lens maker formula is provided here so that aspirants can understand the concept more effectively.
A lens is a transparent medium bounded by two curved surfaces usually spherical or cylindrical , although one of the surfaces of the lens may be a plane. The manufacturer of the lens selects the material of the lens and grinds its surface to make suitable radii of curvatures. He can therefore adjust the focal length of the lens. The lens maker's formula is a mathematical equation that relates the focal length of a thin lens to its refractive index and the radii of curvature of its two surfaces. It is given by the following equation:. The formula can be derived by considering the refraction of light through the lens.
Derive lens makers formula
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Refraction in thin lenses. About About this video Transcript. Let's derive the famous lens makers formula. This formula only works for thin lenses. Created by Mahesh Shenoy. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted. Posted 5 years ago. Downvote Button navigates to signup page. Flag Button navigates to signup page.
Image Formation by Thin Lenses We use ray tracing to investigate different types of images that can be created by a lens.
However, not all lenses have the same shape. The vocabulary used to describe lenses is the same as that used for spherical mirrors: The axis of symmetry of a lens is called the optical axis, where this axis intersects the lens surface is called the vertex of the lens, and so forth. Likewise, a concave or diverging lens is shaped so that all rays that enter it parallel to its optical axis diverge, as shown in part b. To understand more precisely how a lens manipulates light, look closely at the top ray that goes through the converging lens in part a. Likewise, when the ray exits the lens, it is bent away from the perpendicular.
We will discuss the form of the equation that is applicable only to thin lenses. This formula is only applicable to a lens of a given refractive index placed in air. We make the assumption that this is a thin lens as stated earlier , the points D , P and E in figure 1 have a very small distance between them, which can be neglected. Therefore, the radii of curvature of the left side of the lens is the distance C 2 E, approximately the same as the C 2 P — i. Consider the lens setup as shown in Figure 2. O is the point at which the object is placed on the principal axis of the lens.
Derive lens makers formula
A lens is a transparent medium bounded by two curved surfaces usually spherical or cylindrical , although one of the surfaces of the lens may be a plane. The manufacturer of the lens selects the material of the lens and grinds its surface to make suitable radii of curvatures. He can therefore adjust the focal length of the lens. The lens maker's formula is a mathematical equation that relates the focal length of a thin lens to its refractive index and the radii of curvature of its two surfaces. It is given by the following equation:. The formula can be derived by considering the refraction of light through the lens. But before moving directly to the derivation part, first, have a brief review regarding the sign convention adopted and assumptions to be made while doing derivation, which can be found in the later parts of this article only. Example 1. A biconvex lens has radii of 20 cm each. If the refraction Refractive index of the lens material is 1.
Wild horse islands roblox codes
The overall effect is that light rays are bent toward the optical axis for a converging lens and away from the optical axis for diverging lenses. It is best to trace rays for which there are simple ray-tracing rules. The distances of the object and images are measured from the optical center C of the lens. This formula is called the lens maker's formula because it tells what curvature will be needed to make the lens of desired focal length. Write symbols and values on the sketch. Log in. The magnification and orientation of the image are found from. Is the sketch or ray tracing consistent with the calculation? We chose to locate the image base of the arrow, which is on the optical axis. Likewise, when the ray exits the lens, it is bent away from the perpendicular. As for mirrors, ray tracing can accurately describe the operation of a lens. The distance from the center of the lens to its focal point is the focal length f of the lens.
A lens is a transparent medium surrounded by two surfaces, at least one of which must be curved.
In the case of the real image, v is positive and in the case of the virtual image v is negative. Where does the image form and what type of image is formed as the object approaches the lens from infinity? Bhagyashree U Rao. This formula is called the lens maker's formula because it tells what curvature will be needed to make the lens of desired focal length. Image Formation by Thin Lenses We use ray tracing to investigate different types of images that can be created by a lens. Soumya Ranjan Meshwa May 15, at pm. For a converging lens, the point at which the rays cross is the focal point F of the lens. Downvote Button navigates to signup page. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The following example demonstrates this approach.

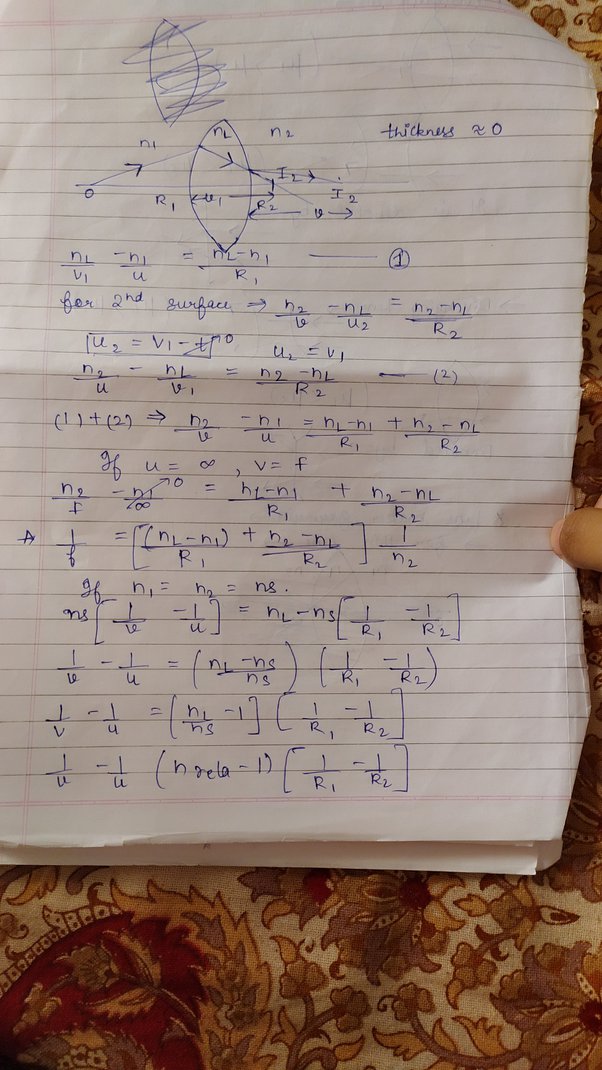
It is a pity, that now I can not express - I am late for a meeting. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.