Enzymes byjus
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete, enzymes byjus. These enzymes are successfully produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications.
The human body is composed of different types of cells, tissues and other complex organs. For efficient functioning, our body releases some chemicals to accelerate biological processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion and a few other metabolic activities to sustain a healthy life. Hence, enzymes are pivotal in all living entities which govern all the biological processes. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. The majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes. Metabolic processes and other chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by a set of enzymes that are necessary to sustain life. The initial stage of metabolic process depends upon the enzymes, which react with a molecule and is called the substrate.
Enzymes byjus
Stay tuned for updated notes by subscribing to the newsletter! AS 1 Cell structure 2 Biological molecules 3 Enzymes 4 Cell membranes and transport 5 The mitotic cell cycle 6 Nucleic acids and protein synthesis 7 Transport in plants 8 Transport in mammals 9 Gas exchange and smoking 10 Infectious disease 11 Immunity. Paper 3 Paper 5 notes are included with theory. Flashcards 1. A2-Level flashcards. YouTube Channels. A-Level specific 1. Tailored Tutors - Perfect explanations into concepts that have been the easiest to understand for me. SnapRevise - Not my favourite, but some of their videos have been really helpful. Other channels equally as good! Amoeba Sisters - Simple explanations and introductions into more complex topics, perfect for A-Level. CrashCourse - Hank Green is a marvel so it's needless to say his biology videos are top notch.
The applications of enzymes include:. Immobilized enzyme bansalaman
What are enzymes and what do they do in our bodies? Enzymes are basically proteins that are produced by living organisms to bring about certain metabolic and biochemical reactions in the body. They are biological catalysts that speed up reactions inside the body. Enzymes, as mentioned above, are biological catalysts. While they hasten or speed up a process, they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process.
Enzymes are biological catalysts which act to increase the rate of a reaction without being used up or changed themselves. They are specific to one type of reaction and one, or a small number of, closely related reactants known as substrates. Enzymes are a vital component of the cell as without them, many biological reactions would be too slow to sustain life. Enzyme kinetics is the study of enzyme reaction rates and the conditions which affect them. In this article, we will discuss the structure and function of enzymes, their clinical significance and theories of enzyme kinetics. Enzymes are proteins and usually have a globular tertiary structure. Their structure is highly specific to the reaction they catalyse, and hence the reactants involved, due to the presence of an active site where the reaction itself occurs. This is a small cleft within the enzyme with a specific amino acid structure allowing the substrate to bind and form the enzyme-substrate complex ES , which is held together by weak bonds to allow dissociation of the complex when the reaction is finished. The rest of the enzyme acts as a scaffold, bringing these key amino acids together.
Enzymes byjus
Enzymes help with specific functions that are vital to the operation and overall health of the body. They help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. They are essential for respiration, digesting food, muscle and nerve function, and more. Each cell in the human body contains thousands of enzymes. Enzymes provide help with facilitating chemical reactions within each cell. The majority of enzymes are proteins, though some are Ribonucleic acid RNA molecules. Enzymes help with the chemical reactions that keep a person alive and well. For example, they perform a necessary function for metabolism, the process of breaking down food and drink into energy. Enzymes speed up catalyze chemical reactions in cells. More specifically, they lower the threshold necessary to start the intended reaction.
Legendarylootz face
Introduction to Enzyme biotechnology. In this case A is the first substrate and B being the second substrate. What are enzymes and what do they do in our bodies? Download the App Watch lectures, practise questions and take tests on the go. Immobilization techniques saranyasaranya Cleland, Wallace. This theory states that the substrate fits exactly into the active site of the enzyme to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The biochemical reactions occurring in the body are basically of 6 types and the enzymes that bring about these reactions are named accordingly:. There are approximately different enzymes found in human cells, which include amylase, pepsin, trypsin, pancreatic lipase, ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease. A cofactor is essential for the functioning of an enzyme.
Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins.
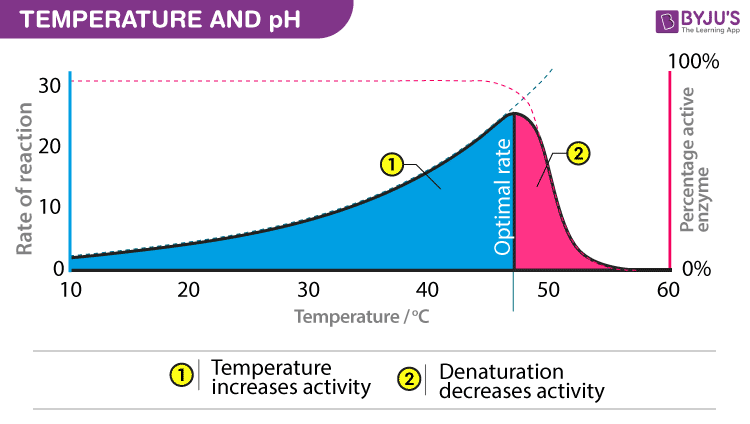
Then one can observe that the bread gets puffed up as a result of fermentation of the sugar by the enzyme action in yeast, which leads to the formation of carbon dioxide gas. As enzymes are functional in cells, the feasible conditions for nearly all enzymes are temperatures that are moderate. Enzyme of immobilization by kk sahu. Enzymes are a linear chain of amino acids, which give rise to a three-dimensional structure. An immobilized enzyme is one whose movement in space has been restricted either completely or to a small limited region. For any reaction to occur in the universe, there is an energy requirement. They do so in the transition state. Also Read- Digestion process in Ruminants. Only a small section of the structure is involved in catalysis and is situated next to the binding sites. At higher temperatures, given a specific point, there is a drastic decrease in the activity with the denaturation of enzymes. At the end of the reaction the enzyme MUST be found in its original form. Enzyme-substrate interactions induce reactive groups into proximity with one another. Immobilization of plant cells aachal jain. This model also describes why enzymes are so specific in their action because they are specific to the substrate molecules.

Excuse, that I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
Very amusing message
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.