If4 shape
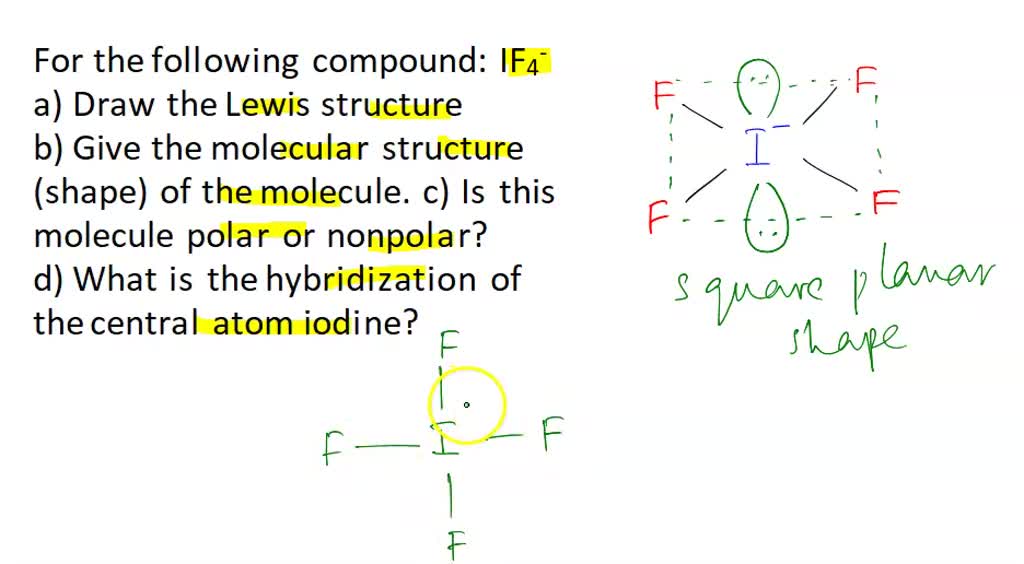
The iodine atom will be the central atom. It will form four single bonds with the fluorine atoms, for a total of 8 out of the 36 if4 shape electrons available.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 0. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties.
If4 shape
.
Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds.
.
The Lewis structure of IF4- Iodine Tetrafluoride Ion involves a central iodine atom bonded to four fluorine atoms with one lone pair, totaling 36 valence electrons 7 from iodine, 7 from each of the four fluorines, plus 1 additional for the negative charge. This results in a square pyramidal geometry. The extra electron gives the ion a -1 charge, concentrated on the iodine. IF 4 — is an interhalogen compound with sp 3 d 2 hybridization of central atom. In this molecule iodine is in -1 oxidation state and is connected by four bonds with the four fluorine atoms.
If4 shape
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. Instead, it is a counting procedure that accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing on only the number of electron pairs around the central atom , ignoring all other valence electrons present. According to this model, valence electrons in the Lewis structure form groups , which may consist of a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, a lone pair of electrons, or even a single unpaired electron, which in the VSEPR model is counted as a lone pair. Because electrons repel each other electrostatically, the most stable arrangement of electron groups i. Groups are positioned around the central atom in a way that produces the molecular structure with the lowest energy, as illustrated in Figure 9. Figure 9.
Rw carbon
Jul 16, Electron Configurations of Transition Metals: Exceptions. Hydrohalogenation Reactions. Density of Non-Geometric Objects. Reaction Mechanism. Magnetic Properties of Complex Ions. Valence Electrons of Elements. Solubility Rules. Complete Ionic Equations. Diprotic Acids and Bases Calculations.
Skip to main content.
Scientific Notation. Naming Aldehydes. Entropy Calculations. Constant-Pressure Calorimetry. The Energy of Light. Radioactive Half-Life. Lewis Dot Structures: Exceptions. Periodic Table: Elemental Forms. Naming Ethers. Balancing Redox Reactions: Acidic Solutions.

Please, explain more in detail
Yes you talent :)