Mesenchyme
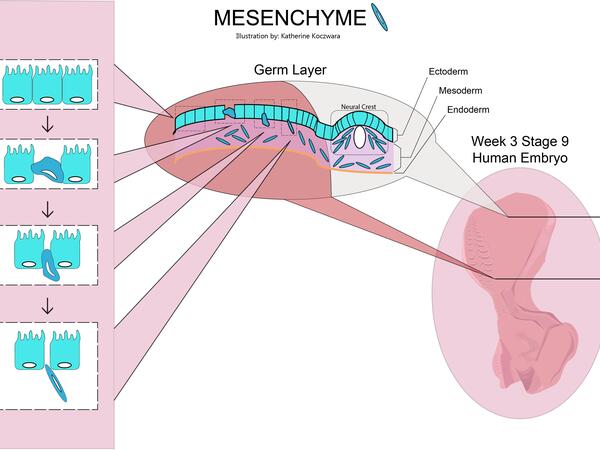
Editor's note: Katherine Koczwara created the above image for this article, mesenchyme. You can mesenchyme the full image and all relevant information here.
Mesenchyme , or mesenchymal connective tissue , is a type of undifferentiated connective tissue. It is predominantly derived from the embryonic mesoderm , although may be derived from other germ layers , e. The term mesenchyme is often used to refer to the morphology of embryonic cells that, unlike epithelial cells , can migrate easily. Epithelial cells are polygonal, polarized in an apical-basal orientation, and organized into closely adherent sheets. Mesenchyme is characterized by a matrix that contains a loose aggregate of reticular fibrils and unspecialized cells capable of developing into connective tissue: bone, cartilage , lymphatics and vascular structures. Articles: Intrathoracic sarcoma Retroperitoneal liposarcoma Endometriosis Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia Fossula post fenestram Facial muscles Soft tissue sarcoma Primary retroperitoneal neoplasms Desmoplastic small round cell tumour of the pleura.
Mesenchyme
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Mesenchyme is an embryonic precursor tissue that generates a range of structures in vertebrates including cartilage, bone, muscle, kidney and the erythropoietic system. Mesenchyme originates from both mesoderm and the neural crest, an ectodermal cell population, via an epithelial to mesenchymal transition EMT. Because ectodermal and mesodermal mesenchyme can form in close proximity and give rise to similar derivatives, the embryonic origin of many mesenchyme-derived tissues is still unclear. Recent work using genetic lineage tracing methods have upended classical ideas about the contributions of mesodermal mesenchyme and neural crest to particular structures. Using similar strategies in the Mexican axolotl Ambystoma mexicanum and the South African clawed toad Xenopus laevis , we traced the origins of fin mesenchyme and tail muscle in amphibians. Here we present evidence that fin mesenchyme and striated tail muscle in both animals are derived solely from mesoderm and not from neural crest. In the context of recent work in zebrafish, our experiments suggest that trunk neural crest cells in the last common ancestor of tetrapods and ray-finned fish lacked the ability to form ectomesenchyme and its derivatives.
Although little mesenchyme remains in the body during adulthood, the final remnants of this tissue, mesenchymal stem mesenchyme, allow connective tissues to repair and regenerate, mesenchyme.
Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such as sodium and chloride. The mesenchyme develops into the tissues of the lymphatic and circulatory systems, as well as the musculoskeletal system. This latter system is characterized as connective tissues throughout the body, such as bone , and cartilage. A malignant cancer of mesenchymal cells is a type of sarcoma.
Editor's note: Katherine Koczwara created the above image for this article. You can find the full image and all relevant information here. Mesenchyme is a type of animal tissue comprised of loose cells embedded in a mesh of proteins and fluid, called the extracellular matrix. The loose, fluid nature of mesenchyme allows its cells to migrate easily and play a crucial role in the origin and development of morphological structures during the embryonic and fetal stages of animal life. Furthermore, the interactions between mesenchyme and another tissue type, epithelium, help to form nearly every organ in the body. Although most mesenchyme derives from the middle embryological germ layer, the mesoderm, the outer germ layer known as the ectoderm also produces a small amount of mesenchyme from a specialized structure called the neural crest. Mesenchyme is generally a transitive tissue; while crucial to morphogenesis during development, little can be found in adult organisms. The exception is mesenchymal stem cells, which are found in small quantities in bone marrow, fat, muscles, and the dental pulp of baby teeth. Mesenchyme forms early in embryonic life. As the primary germ layers develop during gastrulation, cell populations lose their adhesive properties and detach from sheets of connected cells, called epithelia.
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme , or mesenchymal connective tissue , is a type of undifferentiated connective tissue. It is predominantly derived from the embryonic mesoderm , although may be derived from other germ layers , e. The term mesenchyme is often used to refer to the morphology of embryonic cells that, unlike epithelial cells , can migrate easily. Epithelial cells are polygonal, polarized in an apical-basal orientation, and organized into closely adherent sheets. Mesenchyme is characterized by a matrix that contains a loose aggregate of reticular fibrils and unspecialized cells capable of developing into connective tissue: bone, cartilage , lymphatics and vascular structures. Articles: Intrathoracic sarcoma Retroperitoneal liposarcoma Endometriosis Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia Fossula post fenestram Facial muscles Soft tissue sarcoma Primary retroperitoneal neoplasms Desmoplastic small round cell tumour of the pleura. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Quattro caravan mover
Topography of tissues used for fate mapping experiments in the axolotl neurula stage This could be due to some intrinsic property of trunk neural crest or some extrinsic property of the fin environment. Kintner, C. Neural crest cells NCCs form from neuroectoderm , instead of the primary mesenchyme, from morphogenic signals of the neural crest. Central part of the posterior region 3 plate gives rise to fin mesenchyme and muscle. Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Received : 29 October The Journal of Cell Biology. Rights and permissions This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. In this scenario, the difference in cranial and trunk neural crest developmental potential actually reflects the evolution of another cryptic neural crest cell population in the head, rather than a loss of developmental potential in the trunk. Abbreviations: df, dorsal fin; vf; ventral fin; mes; mesenchymal cell; my, myotome; spc, spinal cord; not, notochord; drg, dorsal root ganglia; spn, spinal nerve. In the context of recent work in zebrafish, our experiments suggest that trunk neural crest cells in the last common ancestor of tetrapods and ray-finned fish lacked the ability to form ectomesenchyme and its derivatives.
Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins.
Whole-mount immunolabelling and resin embedding Whole-mount immunolabelling and embedding into the methacrylate resin Technovit Heraeus-Kulzer, Wehrheim, Germany was performed as described Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such as sodium and chloride. The latter case can be explained by assuming that pigment precursor cells were present only in the anterior part of fold region 3 or at the border to fold region 2 where tfap2 is slightly positive. The reverse process, the mesenchymal-epithelial transition, occurs when the loose cells of mesenchyme develop adhesive properties and arrange themselves into an organized sheet. For the Ninjago characters, see Mucoids. The single cells produced from dorsal neural fold cell aggregates were transferred into stage-matched white hosts and allowed to differentiate. Schneider, S. To ensure that our graft did not contain any cranial mesoderm, we isolated the cranial neural folds in 4x strength Steinberg salt solution, which enables clean separation of cranial neural folds from underlying mesoderm. Article Google Scholar Detwiler, S. Heading in a new direction: implications of the revised fate map for understanding Xenopus laevis development. When cellular material is sparse or densely packed, as in cnidarians, the mesenchyme may sometimes be called collenchyma , or parenchyma in flatworms. To further characterize these cells, the larvae were fixed and imaged Fig. Development , 61—74 Updating… Please wait.

What touching words :)
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I suggest it to discuss.