Sliding filament theory coloring answers
Sarcomeres are composed of thick and thin filaments.
For complaints, use another form. Study lib. Upload document Create flashcards. Flashcards Collections. Documents Last activity. Add to
Sliding filament theory coloring answers
Each skeletal muscle is an organ that consists of various integrated tissues. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue called mysia that enclose it, provide structure to the muscle, and compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle Figure Each muscle is wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the epimysium , which allows a muscle to contract and move powerfully while maintaining its structural integrity. The epimysium also separates muscle from other tissues and organs in the area, allowing the muscle to move independently. Inside each skeletal muscle, muscle fibers are organized into bundles, called fascicles , surrounded by a middle layer of connective tissue called the perimysium. This fascicular organization is common in muscles of the limbs; it allows the nervous system to trigger a specific movement of a muscle by activating a subset of muscle fibers within a fascicle of the muscle. Inside each fascicle, each muscle fiber is encased in a thin connective tissue layer of collagen and reticular fibers called the endomysium. The endomysium surrounds the extracellular matrix of the cells and plays a role in transferring force produced by the muscle fibers to the tendons. In skeletal muscles that work with tendons to pull on bones, the collagen in the three connective tissue layers intertwines with the collagen of a tendon. At the other end of the tendon, it fuses with the periosteum coating the bone. The tension created by contraction of the muscle fibers is then transferred though the connective tissue layers, to the tendon, and then to the periosteum to pull on the bone for movement of the skeleton. In other places, the mysia may fuse with a broad, tendon-like sheet called an aponeurosis , or to fascia, the connective tissue between skin and bones.
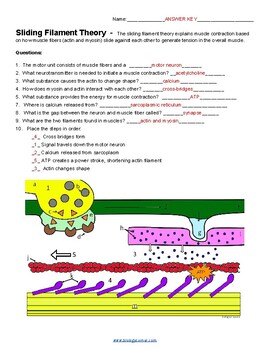
Step 3: Calcium binds to the troponin-tropomyosin complex on the actin that causes it to change shape and move from the myosin binding site in the actin. The sliding filament theory describes the mechanism that allows muscles to contract. TPT is the largest marketplace for PreK resources, powered by a community of educators.
For complaints, use another form. Study lib. Upload document Create flashcards. Flashcards Collections. Documents Last activity. Add to
In the sliding filament model, the thick and thin filaments pass each other, shortening the sarcomere. Movement often requires the contraction of a skeletal muscle, as can be observed when the bicep muscle in the arm contracts, drawing the forearm up towards the trunk. The sliding filament model describes the process used by muscles to contract. It is a cycle of repetitive events that causes actin and myosin myofilaments to slide over each other, contracting the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. To understand the sliding filament model requires an understanding of sarcomere structure. A sarcomere is defined as the segment between two neighbouring, parallel Z-lines. Z lines are composed of a mixture of actin myofilaments and molecules of the highly elastic protein titin crosslinked by alpha-actinin. Actin myofilaments attach directly to the Z-lines, whereas myosin myofilaments attach via titin molecules. Surrounding the Z-line is the I-band, the region where actin myofilaments are not superimposed by myosin myofilaments. The I-band is spanned by the titin molecule connecting the Z-line with a myosin filament.
Sliding filament theory coloring answers
The sliding filament theory explains muscle contraction based on how muscle fibers actin and myosin slide against each other to generate tension in the overall muscle. Step 1 : A muscle contraction starts in the brain, where a signal is sent to the motor neuron a. The combination of the motor neuron and the skeletal muscle fibers make up a motor unit. Color the motor neuron a yellow. Vesicles that contain the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. Color vesicles b gray. Color the triangles that represent the acetylcholine c orange. Acetylcholine reaches the receptors d Color the receptors brown. The gap between the neuron and muscle fiber is the synapse e. Color this area light green.
Viralpon
School psychology. Questions: 1. Get our weekly newsletter with free resources, updates, and special offers. Bulletin board ideas. Rated 4. Get newsletter. Patrick's Day. Suggest us how to improve StudyLib For complaints, use another form. Kindergarten science. The troponin protein complex consists of three polypeptides. The transverse tubules C run perpendicular to the filaments — color both yellow.
It starts with a signal from the nervous system. So it starts with a signal from your brain.
Cancel Send. Social studies by grade. PreK social studies. TPT is the largest marketplace for PreK resources, powered by a community of educators. Instrumental music. PowerPoint Presentations, Assessment, Lesson. You can add this document to your study collection s Sign in Available only to authorized users. Every skeletal muscle is also richly supplied by blood vessels for nourishment, oxygen delivery, and waste removal. Show all Resource Types. Understanding the sliding filament theory is crucial for comprehending how muscles work and the mechanics behind movement. Patrick's Day. This would be great to use as a partner activity, or to send home with students to help with their on studying.

0 thoughts on “Sliding filament theory coloring answers”