Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium -mediated plant transformation has been used widely, but there are plants that are recalcitrant to this type of transformation. It is desirable to develop strains that can broaden the host range. A large number of Agrobacterium strains have not been tested yet to determine whether they can be used in transformation.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ». A tumor- inducing hence the acronym plasmid found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens q. It is these hormones that cause gall formation. Only a small part of the plasmid actually enters the plant; the rest stays in the bacterium, where it has other functions. The wild-type plasmid produces tumor cells, but it can be modified so that it can carry foreign genes into cells without making the recipient cells tumorous. Ti-mediated tumorigenesis is the first case of a horizontal mobile element q. See Chronology, , Zaenen et al. From: Ti plasmid in A Dictionary of Genetics ». Subjects: Science and technology — Life Sciences. View all related items in Oxford Reference ». Search for: 'Ti plasmid' in Oxford Reference ». All Rights Reserved.
The difference in the auxiliary vir region affects the host range in part. Characteristics analyzed were opine type, amplification of vir gene fragments, and PCR-RFLP banding patterns for the long vir and tms fragments. Rose isolates of A.
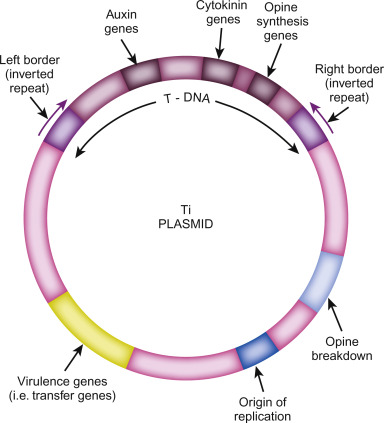
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium.
Ti-Plasmid is also known as an extrachromosomal genetic material found in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The crown ball disease that affects dicot plants is caused by this phytopathogen. The size of the Ti Plasmid is kb. These are large plasmids that typically have a size between kbp and 2 Mbp. Ti Plasmid is an extrachromosomal genetic material found in the dicot plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. This phytopathogen causes crown ball disease, which is a problem for dicot plants. A useful tool for transferring desired genes to different plant species, the Ti Plasmid was initially discovered in These Plasmids can range in size from Kbps to 2 Mbps, which is often rather large. Because they only replicate at one spot, they are also frequently referred to as replicons.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The trb operon from pTiC58 is one of three loci that are required for conjugal transfer of this Ti plasmid. The operon, which probably codes for the mating bridge responsible for pair formation and DNA transfer, contains 12 genes, 11 of which are related to genes from other members of the type IV secretion system family. Insertion mutations were constructed in each of the 12 genes, contained on a full-length clone of the trb region, using antibiotic resistance cassettes or a newly constructed transposon. This transposon, called mini-Tn 5 P trb , was designed to express genes downstream of the insertion site from a promoter regulated by TraR and AAI. Each mutation could trans complement downstream Tn 3 HoHo1 insertions in the trb operon of full-sized Ti plasmids. However, these mutants retained residual conjugal transfer activity when tested in strain NT1, which contains this large plasmid.
Diver r fins
Agropine was synthesized as described previously All isolates were pathogenic and induced the formation of galls when inoculated on rose and tobacco plants. Ohta, S. This process utilizes preexisting gaps in the host plant cell's genome to allow the T-DNA to pair with short sequences in the genome, priming the process of DNA ligation , where the T-DNA is permanently joint to the plant genome. Blanchard, et al. The presence of this Ti plasmid is essential for the bacteria to cause crown gall disease in plants. Galls from roots and rootstocks of the same plant were treated separately. Hardayani, M. The results indicate that rootstocks from breeder C or D were the source for the dissemination of the succinamopine-type isolates that we found in rose plants from 14 independent flower producers. Viroid Pospiviroidae Avsunviroidae. Formation of deletional derivatives of the Ti-plasmid pGV in a conjugative transfer from Agrobacterium tumefaciens to Escherichia coli. In grapevine, A. See Chronology, , Zaenen et al. Agrobacterium Conn Gelvin and R.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Octopine Ti-plasmid deletion mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens with emphasis on the right side of the T-region. The two strains of A. To our knowledge, the present study represents the first demonstration of a close correlation between the Ti plasmid type of A. RFLP analysis of amplified vir and vir The open bars indicate specific GUS activity. Twenty-four samples were obtained from flowering, grafted plants. Members of this family have a characteristic repABC gene cassette. Plasmid DNA was extracted from each E. Willems A, Collins M D. We thank Neil Ledger for editorial assistance. Binary vector with nptII driven by P nos ; Km r. Km r calluses were induced in tobacco frequently by C58C1 strains containing this plasmid and less frequently by A4RL strains containing the same disarmed plasmid. Hardayani, M. Uraji, N.

Bravo, what necessary words..., a brilliant idea
I apologise, but it not absolutely approaches me.