What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy
To define electron gain enthalpysometimes, it is also called Electron affinityalthough there exists a small difference between them. The amount of energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom is characterised as an electron gain enthalpy. During the addition of the electron, either the energy can be released or absorbed.
Electron gain enthalpy is nothing but the energy related to an affinity for the electron of an element. It is a tendency of an element towards electron addition to its outermost shell. The addition of electrons is not so easy as it is an energy-dependent process. The entire process is carried out with an element in its gaseous state. The size of the element has a great impact on the electron gain enthalpy as the nuclear attraction force on the valence shell varies with the size of an element. In this Chemistry article, you will get an idea about the Electron gain enthalpy in detail.
What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy
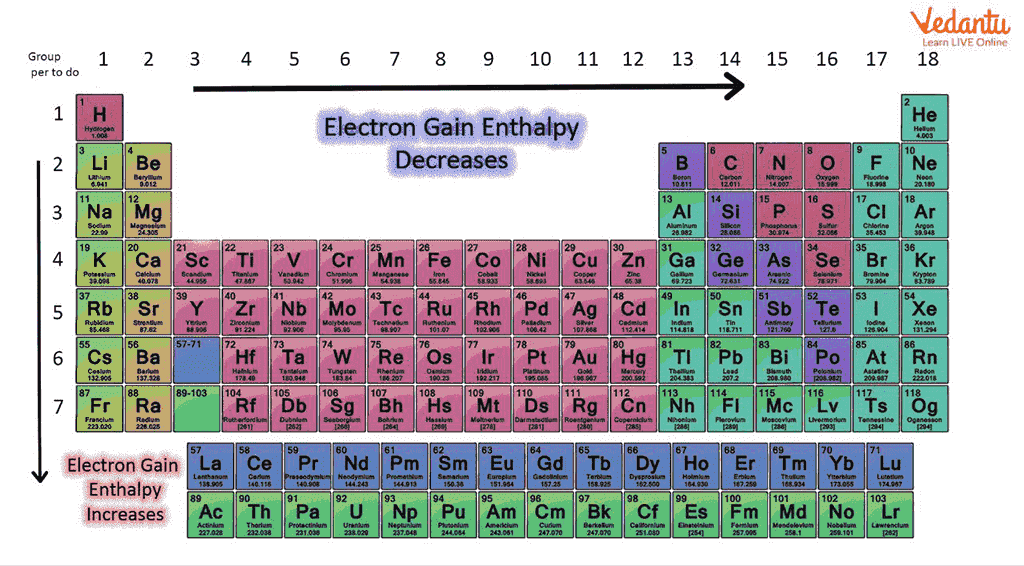
The electron gain enthalpy is an indication of the ability of an atom in gaseous state to release its energy when it gains electrons. It is used in many chemical and physical processes, including photosynthesis and combustion. In general, molecules with higher negative electron gain enthalpies are more reactive and can release energy more easily. The value is negative if the energy is released exothermic and positive if the energy is absorbed endothermic. The electron affinity of an atom is the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. In chemistry, electron gain enthalpy is the change in enthalpy that accompanies the addition of an electron to an atom gaseous state. In general, the negative EGA decreases as the atomic number of the element increases in a group. This trend is due to the increasing size of the atom, which decreases the attractive force between the nucleus and electrons. The electron gain enthalpy is also affected by shielding electrons between the nucleus and electron which we are observing. If the number of shielding electrons increases the effective nuclear charge decreases and negative electron gain enthalpy also decreases. Electron Gain Enthalpy.
The electron gain enthalpy trends that occur in electron gain enthalpy values within a period are irregular for elements of groups 2, 15 and what do you mean by electron gain enthalpy since they have atoms having symmetrical configuration having half-filled and filled orbitals in the same subshell and thus do not have any urge to take up the extra electrons because their configuration will become either less stable or unsymmetrical. Some external energy is needed to add the electron in their atoms.
Electron gain enthalpy is sometimes also referred to as Electron affinity although there is a minute difference between them. Electron gain enthalpy is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom. During the addition of an electron, energy can either be released or absorbed. Let us consider two metals Magnesium and Sodium. Metals lose electrons to obtain the inert gas configuration.
How many of you are aware of what electrons are? But, what is electron gain enthalpy? Well, not anymore! In this chapter, we will look at the concept of electron gain enthalpy and discuss it in greater detail. Electron gain enthalpy of an element is the energy released when a neutral isolated gaseous atom accepts an extra electron to form the gaseous negative Ion i. Greater the amount of energy released in the above process , higher is the electron gain enthalpy of the element. The electron gain enthalpy of an element is a measure of the firmness or strength with which an extra electron is bound to it. It is measured in electron volts per atom or kJ per mole.
What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy
The reaction can be given as below:. On the basis of the nature of the element, the process of accepting electrons in an atom can either be exothermic or endothermic. In general, energy is released when an electron is added to an atom and the electron gain enthalpy for such elements is negative.
Bham weather forecast 10 days
In general, molecules with higher negative electron gain enthalpies are more reactive and can release energy more easily. The electron gain enthalpy of halogens is extremely negative because they can accept the additional electron and get the closest stable noble gas configuration. How can enthalpy change be determined for an aqueous solution? Explore SuperCoaching Now. Due to enhancement of elemental size electron gain enthalpy decrease down the group. So, we will apply the energy in both cases, but the amount of energy required in the case of Magnesium will be lesser compared to Sodium because of the help we are receiving from the nuclear charge of Magnesium in electron attraction. The higher the electron affinity, the more energy is released and the more likely it is that an atom will accept an electron. So, we will apply energy in both the cases but the amount of energy needed in the case of Magnesium will be lesser than that of Sodium because of the help we are receiving from the nuclear charge of Magnesium in attracting the electron. It can be positive or negative. As a result, atoms with more positive nuclear charges tend to have higher electron affinities. Difference Between Electron Gain Enthalpy and Electronegativity Some important differences between electron gain enthalpy and electronegativity are listed below. As a result, energy has to be supplied to add on additional electrons. Electronegativity is defined as the tendency of the atom of an element in a chemical compound to attract a shared pair of electrons towards it in a covalent bond. When an electron is added to an atom, the process can be either endothermic or exothermic.
Electron gain enthalpy is sometimes also referred to as Electron affinity although there is a minute difference between them.
Last updated on Mar 1, Learn more topics related to Chemistry. What Is Iron. The effective nuclear charge can also be reduced by the shielding effect of electrons present in an atom which is gaining electrons. Atomic Size. By this, we can conclude that electron gain enthalpy completely depends on the nuclear charge and atomic radius. Elements with exactly half filled or completely filled orbitals are very stable. By using the thermodynamic concept, we can find a relationship between electron gain enthalpy and electron affinity. Frequently asked questions. It means,. Whereas, if the atom is reluctant to gain an electron, it means it has a negative tendency to gain the electron and is forced to accept it; its electron gain enthalpy is said to be positive. Join courses with the best schedule and enjoy fun and interactive classes. In general, the negative EGA decreases as the atomic number of the element increases in a group.

0 thoughts on “What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy”